Author(s): A Krishna Sailaja* and N Manisha
Rheumatoid arthritis is basically an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of joints and other areas of the body. It is known to affect people of all ages but the main cause of rheumatoid arthritis is still not known precisely among individuals. In RA the joints are damaged to a huge extent that ultimately leads to its destruction and deformity. Although RA has no proper cure it can be treated well under good medications with sufficient rest and regular exercises and occasionally surgery.
Arthritis is still a challenge for medical research. Pharmaceutical research has resulted in several new approaches for treatment/management of arthritis including drugs like the biologic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs). Several disadvantages like serious side effects, high costs and requirement of parenteral administration still invite more research in this area to provide a convenient, affordable therapy with lesser or no side effects. Traditionally used herbal medicines, due to their anti-inflammatory and immune modulatory properties, have potential to be a therapy of choice for arthritis patients and are now extensively being studied. Although a number of these medicines are being used traditionally for their therapeutic activity, development of their novel drug delivery systems was not attractive to the scientists due to insufficient knowledge about their exact mechanism of action and difficulties in processing, standardising, extracting and identification of active constituents. The present manuscript focuses on herbal medicines for arthritis along with various strategies adopted by scientists so as to improve the bioavailability, stability and to reduce the side effects of these medicines so as to provide consistently effective alternative medication for arthritis. A possible way to achieve this is designing novel drug delivery systems for herbal constituents. Novel drug delivery systems help to the reduce toxicity and increase the bioavailability thereby improving the therapeutic value of the active constituent.
‘Rheumatism’means Musculo Skeletal illness, ’Arth’ means joint and ‘itis’ means inflammation.
Rheumatoid arthritis is the most common inflammatory arthritis and is a major cause of disability. It was known to exist in early Native American populations about several hundred years ago but might not have appeared in Europe until the seventeenth century. Early theories on the pathogenesis of Rheumatoid arthritis focused on autoantibodies and immune complexes and the contribution of autoantibodies has returned to the forefront more recently. Based on the pathogenic mechanisms specific therapeutic interventions can be designed to suppress synovial inflammation and joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. There are so many medicinal plants that have shown anti-rheumatoid arthritis properties. So the plants and plant products with significant advantages are used for the treatment of Rheumatoid arthritis (1).
The pathophysiology of OA and RA is distinct although the primary manifestations of both involve the joints. OA is characterized by progressive cartilage loss. Increased thickness of the subchondral plate, osteophytes and subchondral bone cysts are the characteristic features. Vascular invasion and further calcification of nearby articular cartilage may occur as the disease progresses, leading to decreased thickness of articular cartilage. Bone remodeling and enhanced cartilage deterioration takes place over time. The inflammation is generally milder in severity than that observed in rheumatoid arthritis and typically involves the periarticular tissues.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, autoimmune syndrome. Autoimmune inflammation is a result of a response to self-antigens. Thus, a dysregulated immune system results in autoimmune diseases. Synovial inflammation leading to cartilage and bone damage is characteristic of the disease. Persistent inflammation leads to progressive destruction of articular and periarticular structures which in turn, lead to deformity. Morning stiffness is a common problem for patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Characteristic features of RA pathophysiology are increased angiogenesis, cellular hyperplasia, influx of inflammatory cells, changes in the expression of cell surface adhesion molecules and presence of many cytokines. Tumour necrosis factor (TNF) and interleukin-1 are in abundance in the joints. They are the stimulators of proliferation, metalloproteinase expression, adhesion molecule expression, and further secretion of other cytokines. CD4 T cells, mononuclear phagocytes, fibroblasts, osteoclasts, and neutrophils play major role in pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Presence of anti-cyclic citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA) and rheumatoid factor (RF) is highly specific for RA (2).
Warm, swollen joints
• Symmetrical pattern of affected joints
• Fatigue, occasional fevers, loss of energy.
• Joint inflammation often affecting the wrist and finger joints
• Joint inflammation sometimes affecting the joints in the neck,
shoulders, elbows,
• hips, knees, ankles and feet (3).
• Affects 1-3% of the population world wide
• With the peak prevalence between the ages of 30 to 50 years
• Women’s are affected 3 or 4 times more commonly than men.
• Arthritis represents one of the most prevalent chronic health
problems and is a leading cause of disability.
• Arthritis affected 43 million U.S. adults in 2002 and by
the year 2020, this number is expected to reach 60 million.
It is up to three times more common in smokers than non
smokers, particularly in men, heavy smokers, and those who
are rheumatoid factor positive.
• A study in 2010 found that those who drank modest amounts of
alcohol regularly were four times less likely to get rheumatoid
arthritis than those who never drank (4).
There is no definite cause of arthritis. Causes of arthritis depend
upon the particular form of arthritis .Probable of arthritis cause are:
• Genetic susceptibility
• An immunological reaction: possible involving a foreign
antigen , preferentially focused on synovial tissue
• An inflammatory reaction in joints and tendons sheaths
• The appearance of rheumatoid factor in the blood and
synovium
• Articular cartilage destruction
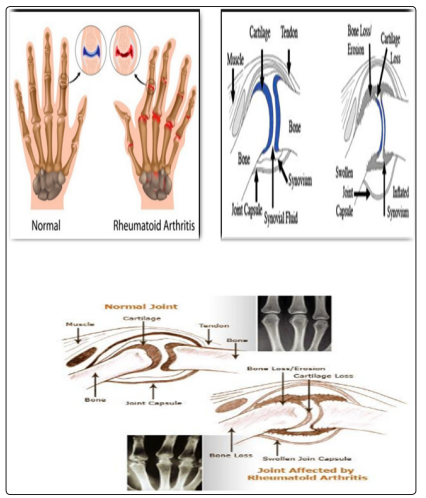
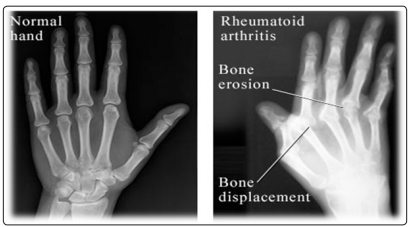
Figures: show comparison of normal joint and joint affected by rheumatoid arthritis.
Generally, over-the-counter medications are recommended first:
1. Acetaminophen (Tylenol) is usually tried first. It is advisable
not to take more than the recommended dose or do not take
the drug along with a lot of alcohol. Doing so may damage
liver.
2. Aspirin, ibuprofen, or naproxen are nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) that can relieve arthritis
pain. However, they have many potential risks, especially
if used for a long time. Potential side effects include heart
attack,stroke, stomach ulcers, bleeding from the digestive
tract, and kidney damage.
| Treatment | Drugs |
|---|---|
| Over The Counter | Acetaminophen (Tylenol), Aspirin, ibuprofen, or naproxen |
| Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) |
Methotrexate, gold salts, penicillamine, sulfasalazine, and hydroxychloroquine. Common combinations of DMARDs include methotrexate -hydroxychloroquine, methotrexate -sulfasalazine, sulfasalazine -hydroxychloroquine, and methotrexate -hydroxychloroquine -sulfasalazine. |
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) |
Paracetamol, ibuprofen, naproxen, meloxicam, etodolac, nabumetone, sulindac, tolementin, choline magnesium salicylate, diclofenac,diflusinal, indomethicin, ketoprofen, oxaprozin, and piroxicam. |
| Biological agents | Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) blockers-etanercept (Enbrel), infliximab (Remicade), adalimumab (Humira), certolizumab pegol (Cimzia), golimumab (Simponi)Monoclonal antibodies against B cells - rituximab (Rituxan) |
Exercise Regularly: Gentle exercise can help to strengthen muscles around joints and also helps to fight fatigue.
Relax: Techniques such as hypnosis, guided imagery, deep breathing and muscle relaxation can be done to control.
Yoga: Yoga can help to improve strength and flexibility. The exercises should be performed with caution by people with rheumatoid arthritis who have spinal problems (6).
In some cases, surgery may be done if other treatments have not worked. This may include:
• Arthroplasty to rebuild the joint • Joint replacement, such as a total knee joint replacement
Conventional treatments for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) present a number of problems, in terms of both safety and efficacy. Owing to side effects of synthetic drugs as shown in table many patients look for complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) options in coping with this debilitating disease.
| Sr no: | Drug | Toxicities |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Methotrexate (DMARD’s) | Stomatitis, rash, alopecia, infrequent myelosuppression, hepatotoxicity, rare but potentially life-threatening pulmonary toxicity |
| 2 | Oral Gold Salts | Diarrhoea |
| 3 | Injectable Gold Salts | Stomatitis, myelosuppression, rash, thrombocytopenia |
| 4 | Cyclosporine | Renal impairment, hypertension, gingival overgrowth |
| 5 | D-penicillamine | Rash, stomatitis, dysgeusia, proteinuria, myelosuppression |
| 6 | Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs | Gastrointestinal symptoms (indigestion, ulceration, hemorrhage, stomatitis); renal abnormalities; pulmonary neurological abnormalities; abnormalities; dermatologic abnormalities; hematologic abnormalities; hepatic abnormalities; displacement of protein-bound drugs; possible systemic complication |
Research has indicated that people suffering from chronic pain, as in RA, and those dissatisfied with current treatment are very likely to seek alternative treatments, and an estimated 60-90% of persons with arthritis use CAM. With the growing interest in herbal therapies among persons with rheumatoid arthritis, there exists a need for investigation into their safety and efficacy .The management of rheumatoid arthritis is a multidisciplinary approach in order to lessen the pain, reduction of inflammation and restoration of joints function. In practical terms suppression of inflammation is the target intensive therapy. Herbal medicines have become popular for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis worldwide recently (7).
• Conventional treatments for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) present a number of problems, in terms of both safety and efficacy. Owing
to side effects of synthetic drugs many patients look for complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) options.
• Herbal medicinal drugs that interact with the mediators of inflammation are used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
| Biological | Part used | Active ingredients | Therapeutic uses | Extract |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annona montana. (Annonaceae) |
Leaves, fruit, seeds, bark, roots | Cyclomontanins A-D (1-
4), br
annomuricatin C (5), and (+)-corytuberine |
Anti-rheumatic, anthelmintic, anticonvulsant, antidepressant, antimicrobial, antineoplastic, antiparasitic, antispasmodic, antiviral, astringent |
methanol |
| Asparagus racemosus (Liliaceae) |
Roots, Leaves, flowers and fruits |
Steroidal glycosides
including shatavarins
I-IV, diosgenin and various sterols, alkaloid asparagamine A, flavonoids: quercitin, rutin and hyperoside, an isoflavone, and a mucilage |
Ulcerogenesis, antioxidant, treatment of thirst, fainting, dyspnoea, and gout |
methanol |
| Boswellia serrata Roxb. (Burseraceae) |
Oleogum resin | Resin which is pentacyclic triterpenoid in nature in which boswellic acids (β-boswellic acid, acetyl-βboswellic acid, keto-β-boswellic acid and acetyl-11- keto-βboswellic acid) |
Cancer, inflammation, arthritis, asthma, psoriasis, colitis and hyperlipidemia |
Petroleum ethre |
Certain herbs may have anti-inflammatory properties that can help with rheumatoid arthritis [RA]

• Arnica
• Aurum metallicum
• Bryonia
• Causticum
• Calcarea fluoricum
• Kalmia latiflora
• Ledum palustre
• Rhododendron
Chronic arthritis with a feeling of bruising and soreness may be helped by this remedy. The painful parts feel worse from being moved or touched. The gels and ointments of Arnica may help to soothe arthritic pain when applied externally to areas of inflammation and soreness.

This remedy is prescribed for wandering pains in the muscles and joints that are better from motion and warmth and worse at night. The person may experience deep pain in the limbs when trying to sleep. Therefore people who need this remedy are often serious and focused on work or career with a tendency to feel depressed.
Bryonia is an excellent remedy in cases of acute pains of rheumatoid arthritis. It helps in relieving the chest pains that gets worse while coughing. It may be given when the pains are worse by slightest touch and also when the pains are associated with swelling of the joints.
Causticum that is used in homeopathic treatment of individuals suffering from rheumatoid arthritis has symptoms that include the development of deformities in the joints, contractures and weakness in the muscles of the body in general. These symptoms can be relieved through the use of warm applications and during conditions of cold weather it can lead to the worsening of the pain and the stiffness.
This medicine works for these patients of arthritis who tend to have large or medium joint infections such as knee joint, spine or shoulders. The patients will have pain in waking up in the mornings or while getting up from a sitting position. The joint pains are better by hot applications.
Kalmia is extremely useful in rheumatism that effect the chest. Even inflammatory rheumatism shifting from joint to joint, which tends to attack the heart and also cause high fever and excruciating pain, will be benefitted by kalmia.
The ledum rheumatism begins in the feet and travels upward. The pains of ledum and the purple mottling of the skin, which is a concomitant are almost entirely abated by putting the affected limb in cold water. Ledum maybe indicated in both acute and chronic form of this complaint.
The patients experience rheumatism in hot season where their joints become swollen and there is rheumatic tearing in all limbs. Rhododendron basically helps with rheumatic and gouty symptoms. It prevents stiffness of neck, pain in shoulders, arms, wrists. It also provides relief of swollen joints and gouty inflammation of the great-toe joint.

Plant preparations or their parts have been widely used in medicine since ancient times and till today use of phytomedicines is wide spread. Most of the biologically active constituents of plants are polar or water-soluble. However, water-soluble phytoconstituents are poorly absorbed due to macromolecular size, which cannot be absorbed by passive diffusion or due to their poor lipid solubility, thus severely limiting their ability to transport across lipid-rich biological membranes, resulting in their poor bioavailability.
Phytosomes are defined “Phyto” means plants and some means cell-like, which is a novel drug delivery system, Phytosome is a newly introduced patented technology developed to incorporate the water-soluble phytoconstituents into phospholipids to produce lipid compatible molecular complexes called phytosomes. provide better absorption and bioavailability than the conventional herbal drugs. When a stoichiometric amount of the phospholipid was made to react with purified herbal drug in an aprotic solvent, phytosomes were formed (9).
1. Casperme TM Boswellia phytosome
2. Meriva Turmeric phytosome



These herbal treatments are therefore entirely natural and will definitely reduce the pain and inflammation in the joints. So taking good care of the joints and exercising regularly will help reduce the risk of rheumatoid arthritis. A large number of number of plants described in this , clearly demonstrated the importance of herbal plants in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and also to consider one of good source for a new drug or a lead to make a new drug.
