How the Artificial Intelligence Tool pSumo-CD is Working for Predicting Sumoylation Sites in Proteins
Author(s):
Abstract
Opening the web-server at http://www.jci-bioinfo. cn/pSumo-CD, you will see the top page of pSumo-CD on your computer screen, as shown in Fig.1. Click on the Read Me button to see a brief introduction about this predictor
To see how the web-server is working, please do the
following
Step 1: Opening the web-server at http://www.jci-bioinfo.
cn/pSumo-CD, you will see the top page of pSumo-CD on
your computer screen, as shown in Fig.1. Click on the Read
Me button to see a brief introduction about this predictor
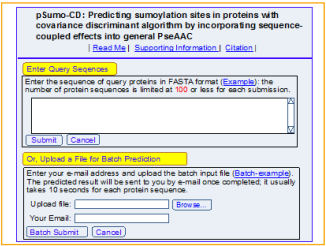
Figure 1: A semi-screenshot of the top-page for the webserver pSumo-CD at http://www.jci-bioinfo.cn/pSumo-CD.
Step 2: Either type or copy/paste your query protein
sequences into the input box at the center of Fig.1: The input
sequences should be in the FASTA format. For the examples
of sequences in FASTA format, click the Example button
right above the input box.
Step 3: Click on the Submit button to see the predicted result. For example, if you use the Sequences in the Example
window as the input, after a few seconds, you will see the corresponding predicted results, which is fully consistent with
experiment observations.
Step 4: Click the Data button to download the benchmark
dataset used in this study.
Step 5: Click the Citation button to find the relevant papers
that document the detailed development and algorithm for
iSuc-PseOpt.
It is anticipated that the Web-Server will be very useful because the vast majority of biological scientists can easily get
their desired results without the need to go through the complicated equations in [1] that were presented just for the integrity in developing the predictor.
Also, note that the web-server predictor has been developed
by strictly observing the guidelines of “Chou’s 5-steps rule”
and hence have the following notable merits (see, e.g., [2, 3]
and three comprehensive review papers [4-6]): crystal clear
in logic development, completely transparent in operation,
easily to repeat the reported results by other investigators,
with high potential in stimulating other sequence-analyzing
methods, and very convenient to be used by the majority of
experimental scientists [1-5].
It has not escaped our notice that during the development
of iSuc-PseOpt web-server, the approach of general pseudo
amino acid components [7] or PseAAC [8] had been utilized and hence its accuracy would be much higher than its
counterparts, as concurred by many investigators (see, e.g.,
[9-10]).
For the marvelous and awesome roles of the “5-steps rule” in
driving proteome, genome analyses and drug development,
see a series of recent papers [11-32] where the rule and its
wide applications have been very impressively presented
from various aspects or at different angles.
References
- J Jia, L Zhang, Z Liu, X Xiao, KC Chou (2016) pSumo-CD: Predicting sumoylation sites in proteins with
covariance discriminant algorithm by incorporating sequence-coupled effects into general PseAAC, Bioinformatics 32: 3133-3141.
- W Hussain, SD Khan, N Rasool, SA Khan, KC Chou
(2019) SPalmitoylC-PseAAC: A sequence-based model
developed via Chou’s 5-steps rule and general PseAAC
for identifying S-palmitoylation sites in proteins, Anal
Biochem 568: 14-23.
- O Barukab, YD Khan, SA Khan, KC Chou (2019) iSulfoTyr-PseAAC: Identify tyrosine sulfation sites by incorporating statistical moments via Chou’s 5-steps rule and
pseudo components Current Genomics http://www.eurekaselect.com/174277/article.
- KC Chou (2011) Some remarks on protein attribute prediction and pseudo amino acid composition (50th Anniversary Year Review, 5-steps rule), J Theor Biol 273:
236-247.
- KC Chou (2019) Advance in predicting subcellular localization of multi-label proteins and its implication
for developing multi-target drugs, Current Medicinal
Chemistry http://www.eurekaselect.com/172010/article 26: 4918-4943.
- KC Chou (2019) Impacts of pseudo amino acid components and 5-steps rule to proteomics and proteome analysis, Current Topics in Medicinak Chemistry (CTMC)
(Special Issue ed. G.P Zhou), http://www.eurekaselect.
com/175823/article.
- KC Chou (2001) Prediction of protein cellular attributes
using pseudo amino acid composition, PROTEINS:
Structure, Function, and Genetics (Erratum: ibid, 2001,
Vol 44, 60), 43: 246-255.
- 8. KC Chou (2005) Using amphiphilic pseudo amino
acid composition to predict enzyme subfamily classes,
Bioinformatics 21: 10-19.
- M Nosrati, H Mohabatkar, M Behbahani (2019) Introducing of an integrated artificial neural network and
Chou’s pseudo amino acid composition approach for
computational epitope-mapping of Crimean-Congo
haemorrhagic fever virus antigens, International Immunopharmacology, or https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1567576919321277.
- . M Tahir, M Hayat, SA Khan (2019) iNuc-ext-PseTNC:
an efficient ensemble model for identification of nucleosome positioning by extending the concept of Chou’s
PseAAC to pseudo-tri-nucleotide composition, Molecular genetics and genomics : MGG 294: 199-210.
- KC Chou (2019) The cradle of Gordon Life Science Institute and its development and driving force, Int J Biol Genetics 1: 1-28.
- KC. Chou (2019) Showcase to illustrate how the
web-server iDNA6mA-PseKNC is working, Journal of
Pathology Research Reviews & Reports 1: 1-15.
- KC Chou (2019) The pLoc_bal-mPlant is a Powerful
Artificial Intelligence Tool for Predicting the Subcellular Localization of Plant Proteins Purely based on their
Sequence Information, Int J Nutr Sci 4: 1-4.
- KC Chou, X Cheng, X Xiao (2019) pLoc_bal-mEuk: predict subcellular localization of eukaryotic proteins by
general PseAAC and quasi-balancing training dataset,
Med Chem 15: 472-485
- KC Chou (2019) Showcase to illustrate how the web-server iNitro-Tyr is working, Glo J of Com Sci and Infor Tec
2: 1-16.
- KC Chou (2019) Gordon Life Science Institute: Its philosophy, achievements, and perspective, Annals of Cancer Therapy and Pharmacology https://onomyscience.
com/onomy/cancer_archive_volume2_issue2.html 2:
001-026.
- KC Chou (2020) Showcase to Illustrate how the webserver pLoc_bal-mEuk Is working, Biomed J Sci & Tech
Res, 24-2.
- KC Chou (2020) The pLoc_bal-mGneg Predictor is a
Powerful Web-Server for Identifying the Subcellular Localization of Gram-Negative Bacterial Proteins based on
their Sequences Information Alone, ijSci 9: 27-34.
- KC Chou (2020) How the artificial intelligence tool iRNA-2methyl is working for RNA 2’-Omethylation sites,
Journal of Medical Care Research and Review 3: 348-
366.
- KC Chou (2020) Showcase to illustrate how the web-server iKcr-PseEns is working, Journal of Medical Care Research and Review 3: 331-347.
- KC Chou (2020) The pLoc_bal-mVirus is a powerful
artificial intelligence tool for predicting the subcellular
localization of virus proteins according to their sequence
information alone, https://medwinpublishers.com/
BPOJ/BPOJ16000130.pdf.
- KC Chou (2019) How the artificial intelligence tool iSNO-PseAAC is working in predicting the cysteine S-nitrosylation sites in proteins, J Stem Cell Res Med 4: 1-9.
- KC Chou (2020) Showcase to illustrate how the web-server iRNA-Methyl is working, J Mol Genet 3: 1-7.
- KC Chou (2020) How the Artificial Intelligence
Tool iRNA-PseU is Working in Predicting the RNA
Pseudouridine Sites, https://biomedres.us/pdfs/BJSTR.
MS.ID.004016.pdf.
- KC Chou (2020) Showcase to illustrate how the web-server iSNO-AAPair is working, https://biomedres.us/pdfs/
BJSTR.MS.ID.004033.pdf.
- KC Chou (2020), The pLoc_bal-mHum is a Powerful
Web-Serve for Predicting the Subcellular Localization of
Human Proteins Purely Based on Their Sequence Information, Adv Bioeng Biomed Sci Res 3: 1-5.
- KC Chou (2020) Showcase to Illustrate How the
Web-server iPTM-mLys is working, Infotext Journal of
Infectious Diseases and Therapy [IJID], 1: 1-16.
- KC Chou (2020) The pLoc_bal-mGpos is a powerful artificial intelligence tool for predicting the subcellular localization of Gram-positive bacterial proteins according
to their sequence information alone, Glo J of Com Sci
and Infor Tec 2: 01-13.
- KC Chou (2020) Showcase to illustrate how the web-server iPreny-PseAAC is working, Glo J of Com Sci and Infor Tec 2: 01-15.
- KC Chou (2020) Some illuminating remarks on molecular genetics and genomics as well as drug development,
Molecular Genetics and Genomics 295: 261-274.
- KC Chou (2020) The Problem of Elsevier Series Journals
Online Submission by Using Artificial Intelligence, Natural Science, 12: 37-38.
- KC Chou (2020) The Most Important Ethical Concerns in Science, Natural Science 12: 35-36.
View PDF

