Author(s): Bekele Shibru
The purpose of the study was to examine the impact of employee turnover on organizational performance of Bekas chemicals PLC. Both descriptive and explanatory research with mixed approach was chosen to study 231 samples from 544 current and ex-employees at Bekas chemicals PLC. Then through SPSS version 25 both descriptive and inferential analysis were made. The study found out that there are high cases of employee turnover in the organization. High rate of employee’s turnover negatively impacted organization performance since most of the experienced and highly productive staffs were lost and it took a long time to recruit new staff. The study concluded that causes of employees’ turnover that impacted negatively on organizational performance are psychological variable which included: job satisfaction and job security. The study recommended that the top management should deign strategies such as increased salaries and remuneration, providing recognition, and other to mitigate the problem.
Employee retention was a major challenge in many organizations. Globally, there is an increase in matters of recruitment and staff retention (Bushe,2012). Employee skills, knowledge, and experience are essential in running an organization. Through human capital, an organization can create and sustain its competitive advantage (Grant, 2010). Implementing an employee retention program is an effective way of ensuring key employees remain in the organization while maintaining job performance, productivity and therefore competitiveness.
Therefore, human resource management is one of the crucial functions that should be carried out in a systematic way so as to maintain well performing employees within the organization. Thus, organizations should have effective human resource management system that is well formulated and implemented to ensure that they hire the right employee and maintain employees who contribute to the successful accomplishment of organization objective.
Employee turnover refers to the rate at which an employer gains and losses employee, how long the staff tend to leave and join the organization. According to Martin (2005) when employees leave the company, the employer has to incur a considerable amount of direct and indirect costs.
On the other hand, a certain degree of labor turnover may be desirable while it enables an organization drop employees with poor performance or negative influence on workplace. In other words, turnover such a case can have positive effect and creates an opportunities to induce wider experience, new ideas to the organization as well as providing career development opportunities for existing workers.
Many previous studies showed that an excessive turnover rate clearly has a tremendous negative impact in an organization’s performance especially when the experienced and skilled ones left [1]. It is so, as the high rate of employee turnover is leads to remain with a large percentage of beginner workers while the expectation its customers are very high due to its reputation.
Voluntary turnover is turnover initiated by employees themselves and it has an adverse effect on performance, service delivery, profit, and on other outcomes that organization set as objectives. It is so as a given replacing a vacancy in an organization takes time and demands cost. On the other hand, the actual practice indicates that most managers don’t give that much of attention to this problem. Turnover costs are important but often hidden from managers as there are no profit and loss statements that specifically capture the “cost of voluntary turnover’. Instead, the costs are buried in line items like recruitment, selection, temporary staffing and training. What is worse was that, the real but unmeasured costs from losses of customer service continuity or critical implicit knowledge are never calculated as illustrated by Abdali (2011).
Similarly, Ahmed, Sabir, Khosa, Ahmad and Bilal (2016) conducted to a study to investigate the impact of employee turnover on the effectiveness of in an organization [2]. In their study, issues such as pay level, firm’s stability, work environment, training opportunity and supervision were among the possible causes of turnover which impacted significantly the performance of the organization. Beside, their study assessed the degree of correlation among the cause of turnover and it was found that they were highly correlated to one another. When it comes to locally made studies, we may find Kumar (2011) who made study at Arba Minch Textile Company and come up with low salary as a main underlying reason; Blen (2018) who made study at Shiltes Garment PLC on employee turnover and organization performance. All these study concluded that lack of training, failure to recognize one’s accomplishment, lack of promotion, poor decision making and supervisor – subordinate relationships, and poor performance appraisal, staying as contract workers for too long; lack of promotional prospects, salaries not being competitive with other institutions, lack of appreciation of the work by management and lack of job security resulted in low commitment which eventually led to increased turnover rate.
According to data compiled Human resource (March 8, 2020) Bekas Chemicals PLC has experiencing high turnover rate each year with average of 23%. Accordingly, the key argument of this study is that if companies do business under such high employee turnover rate, it is not only face a financial cost to the organization, but also detracts the organization from satisfying its customer by not providing adequate services, achieves targets of the organization and reduces individuals and organization’s positive contribution to progressive growth and profitability of company. As a result of the above conceptualization, this research study investigates the impact of employee turnover on the activities of Bekas Chemicals PLC.
To be competent enough in the current global world, every type of organization requires employees who are committed, competent, ethical, motivated and have eagerness to work in that organization. If an organization fails to motivate and retain its experienced and talented employees, profit-making business organizations may face bankruptcy or its survival is under a question. A number of researches were conducted on similar issues out of which Owence et al. (2014) mentioned a number of factors found to be the causes of high turnover such as staying as contract workers for too long; lack of promotional prospects, salaries not being competitive with other institutions, lack of appreciation of the work by management and lack of job security [3].
According to Blen (2018) who made study at Shiltes Garment PLC on employee turnover and organization performance. It was concluded that lack of training, failure to recognize one’s accomplishment, lack of promotion, poor decision making and supervisor-subordinate relationships, and poor performance appraisal, staying as contract workers for too long; lack of promotional prospects, salaries not being competitive with other institutions, lack of appreciation of the work by management and lack of job security resulted in low commitment which eventually lead to increased turnover rate. On the other hand Bekas chemicals PLC introduce attractive salary for all employees annually specially, on November 2018. Nevertheless, According to official records of Human Resource of Bekas chemicals PLC (2020), the company experienced 23% employee turnover rate in average in the last five years. Most desperate was, however, top management still not sure of the reasons why employees are quitting; whether it is related to contract type, promotional prospects, low salary, motivational measures and issues of job security has never been studied. Thus, it remains misunderstood and policy measures are not taken yet is the critical point that initiated the researcher to conduct this research endeavor.
Therefore, this study has been launched to examine the impact of employee turnover on organizational performance taking the case of Bekas chemicals PLC employees using mixed research approach through designing questionnaire and interview guide in searching answer for the following research questions.
The study aims at addressing the following research questions:
This research is designed:
The research is aimed at examining the impact of employee turnover specifically focusing on professional and production staff turnover of Bekas chemicals PLC Adama and Addis Abeba branch. The independent variables considered include Demographic factors, Psychological/push factors, Economic/pull factors, which are conceptualized as causes of employee turnover. On the other hand, organization performance of Bekas chemicals PLC would be measured in terms of efficiency or effectiveness as dependent variables. The study considered the period from 2015-2020. This period is considered to be long enough for the study to understand the performance of the different work units in line with selected performance indicators.
Filipe F and Luis Borges (2012) defined turnover as the rotation of workers around the labor markets; between firms, jobs and occupations; and between the states of employment. According to Robbins (2003) turnover refers to the voluntary and involuntary permanent withdrawal from an organization. Rion (2009) also defined employee turnover as a ratio comparison of the number of employees an organization must replace in a given time period to average number of total employees More over employee turnover does not only include the voluntary termination of employment but also the involuntary termination of membership of an organization.
Voluntary turnover refers to termination initiated by employees. Employee might decide to leave an organization voluntarily because of getting a better job, changing career, or present job is unattractive because of poor working conditions, low pay or benefits, and bad relationship with supervisor (Heneman, Judge, and Kammeyer-Muelle, 2012).
Gomez-Mejia (2014) posits that involuntary turnover is a type of turnover that an organization or employee cannot control [4]. Involuntary turnover occurs when management decides to terminate its relationship with an employee due to economic necessity or a poor fit. Involuntary turnover might occur due to long term sickness, death, or moving overseas (Heneman et al 2012). Employee may leave an organization due to sickness, death, moving abroad or employers-initiated termination (Aman, 2015). Mayhew (2017) argues that involuntary turnover occurs when employers terminate an employee’s contract or ask an employee to resign [5].
Organizational Performance is the process where a firm is able to achieve and sustain profit that exceeds what its competitors are achieving. An organization is able to gain a Organizational Performance over its competitors by understanding its market and customers. It is a situation whereby an organization is able to deliver the same benefits as competitors but at a lower cost (cost advantage), delivers benefits that exceed those of its competitors’ products (differentiation advantage) and creates superior value for its customers Porter, (2010).
There are four domains of organizational performance effectiveness, efficiency, relevance and sustainability. Where effectiveness is achieving results and meeting standards; efficiency is delivering services and increasing reach at lower cost; relevance is engaging target populations plus promoting learning and sustainability is mobilizing resources and increasing social capital (PACT, 2015). The Oxford English Dictionary shows that that organizational performance means the process of performing a task, terms of how successfully it is performed or the capabilities of a machine, product, or vehicle. It may also mean the extent to which an investment is profitable, especially in relation to other investments, (Oxford University Press, 2017). According to Zeeshan et al, (2016), organizational performance is essential for the triumph of an economy [2].
In other way Poor organizational performance in overall can be a lessening in organizational performance level when there had been acceptable level of organizational performance previously. Also it leads to failure to attain an obligatory action level and may as well be a serious reduction in organizational performance extent plus no capacity to partake at expected level or not performing to satisfaction, (Couetil, 2017).
Review of various research studies indicated that employees resign for a variety of reasons. Studies classified the reasons related to demographic, personal, push (controlled) and pull (uncontrolled) factors.
As said by Abdali (2011), the demographic and personnel characteristics of an employee may be reason of leaving from the organization. These characteristics are include; age, gender, qualification, marital status, experience and tenure. According to Parker and Skitmore (2003), top performing females have turnover rates that are 2.5 times those of their male counterparts, a fact that they point out to the demands of balancing work and family life.
In the literature, psychological attitude is one of key areas of push factor which mostly attached with employee turnover decisions. These attitudinal factors that affect employees behavior are classified into job satisfaction, job stress which may cause disturbance that lead to insecure of job. This study wills analysis job satisfaction/dissatisfaction and job security/ insecurity which determine intention to leave or not. If the employees are satisfied with their jobs in terms of roles and duties then there will be no need for them to leave the organization they will work extra hard and hence good performance of the organization. Moreover, (Abdali, 2011) conducted a study on Impact of Employee Turnover on Sustainable Growth of organization in computer Graphics Sector of Karachi, Pakistan. He revealed that Employees want to stay within the organizations just have of clean and healthy environment. In other word Employee job satisfaction is the fulfillment, gratification and enjoyment that come from work. It is not the money or the fringe benefits, but the feelings employees receive from the work itself [6]. Employees determine job satisfaction by comparing the extent to which the outcome meets or exceeds their expectations; this is compared to how co-workers are performing, rewarded and whether there is fairness (Chatzoglou, Vraimaki, Komsiou, Polchrou, and Diamantidis, 2011).
Salary stands as very important factor for Asians to stay in any organization. Survey counts Compensation and benefits as key factor coupled with employees job out of 24 key elements and out of findings, compensation is counted to be the third gratifying aspect of the job. Mostly in Asia people leave their current positions for more pay and external pay equity without much bothering about growth, loyalty and other factors. Higher salary is associated with longer tenure. Compensation/salary forms the basic glittering factor for Asians to switch to next job without much consideration of other factors. Generally, employees compare their job with other organizations in terms of job achievement and compensation (wage), so if one is having recognition that he or she is having more wages and job achievement then this will impact them positively (Choi, 2009).
According to the study of (Philip, Michael P. and Cary L. 2010), The major pull factors are higher rate of pay, more valued benefits package, more job opportunity, better long term career opportunities, a less pressurized environment of work, opportunity to work overseas, shorter distance to travel, more convenient hours of work, desire to work with a colleague, desire to work with particular management team, desire to work with a branded employer, fashioning of CV etc.
Impact of Employee Turnover on Organizational Performance Butali, Wesang and Mamuli (2013) explained that staff turnover is inevitable and is bound to exist in all industrial units even in those organizations where salary and working conditions are extremely attractive and satisfactory [7]. However, high staff turnover is a serious problem and therefore should be treated carefully. High staff turnover adversely affect both employer and employees. The analyses made by Ferreira and Almeida (2015) shown that the consequence of staff turnover in such a way that it is costly for organizations [8]. Every time an employee quits, a replacement must be recruited, selected, trained, and permitted time on the job to gain experience. These costs are not the only negative influences caused of turnover but also it has a tremendous challenge on performance of the organization as well. This challenge may specifically would be much more pronounced when it is a manufacturing industry which is typically identified by a twenty four hours functioning and having different departments which are responsible to get the job done in a stepwise manner. Staff turnover can have a negative effect on an organization performance. It can lead to a loss of productivity, profitability, corporate knowledge, and skills and competencies. In addition, staff turnover is not just an issue for the organization experiencing staff turnover; it can also cause headaches for external organizations communicating with them [7]. Gomez et al, (2010) have stated that employee turnover has somehow negative as well as positive consequences in any organization. To further explain this, the negative consequences can be seen as costs to the organization while the positive consequences are considered as benefit to the organization in a way to avoid incompetent and misbehaving staff members.
On the other hand, performance of organizations encompasses three specific areas of firm outcomes such as financial performance; marketing performance; and shareholder return Linda (2002). More specifically, profit is one of the financial performance measures in the sense that it is a common means of measuring organizations performance. Whereas, finding adequate market share for the products and services of an organization is also considered as one of the performance measures in relation to the marketing aspect of the firm. Besides, there are a numerous factors that affect the performance in the working area. According to some researchers and practitioners, the factor that may affect the performance of employees at work place has an exclusive nature and function of job satisfaction change, or systematic development or weakening in job satisfaction. It was, therefore, concluded that turnover negatively affected by job satisfaction and performance at the same time. The higher the level of satisfaction; the lower the turnover rate is as explained by Kondalkar (2007). Different researchers have showed the adverse relationship between turnover and performance. The notion that turnover decreases the organizational performance was supported by most researchers (Rehman, 2012; Linda, 2002; and 1). Also Linda (2002) suggested that turnover might improve job performance when an employee who planned to quit is being inefficient, as to the study made by Peggy and Bernard (2016),the prevalent relationship between turnover and performances a negative one [9].
According to the study of Ampomah and Cudjor (2015) found out that staff turnover has both positive and negative effects whereby the positive effect include: new ideas and skills being introduced into the company, it opens up promotion channel for employees, it helps in reducing redundancy in the organization and it also helps in replacement of poor performers [10]. And that the negative effect involve: loss of skilled manpower, additional cost of replacement recruitment, poor quality of work and difficulties in attracting new staff affect the organization most. Zeeshan et al, (2016) assert that organizations all over the world are giving more attention and assigning importance to employee turnover as they know that high levels employee’s turnover slow down the performance of the employees as well as of the organization and that it inflates the expenses related to recruitment and new employee training. Mabindisa (2013) adds emphasis that if staff turnover is not taken into consideration, it will cause the productivity of the organization to decrease, customers will lose trust in the organization and that it will damage the image of the organization in addition to the fact that employees will be de motivated to work for an organization with a high staff turnover rate [2].
On the other hand also Kim (2012) has identified staff turnover as costly for the company. According to Dingeer et al, (2012) loosing professional and skilled staff cannot be affordable from the companies and one of the main reason associated with this is also the cost. Now days all over the world organizations have realized the importance of their staff and the impact the staff turnover can have on the performance of the employees and of the organization as well which due to the turnover can be slowed down. The staff turnover impact the increase of the expenses which are related with the recruitment and training of the new staff (Chen, Lin and Lien, 2010).
The aim of the research is to assess impact of employee turnover organization performance with a particular reference to Bekas chemicals PLC. Accordingly, conceptual analysis was done on the basis the independent variables is employee turnover as expressed by factors such as Demographic factors, Psychological/push factors, Economic/pull factors and efficiency or effectiveness as indicators of organizational performance is a dependent variable are operationalized. The figure below shows the proposed conceptual framework adopted by the researcher which are thoroughly dealt in order to come up with relevant information
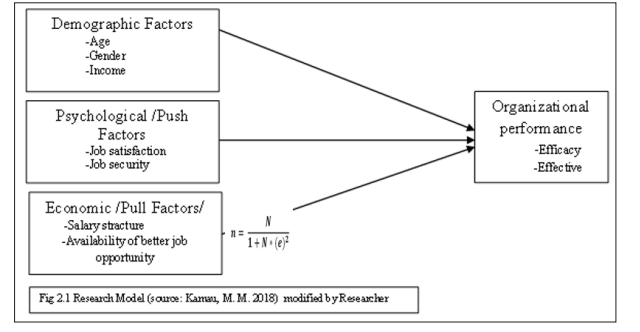
Descriptive and explanatory research design were used in the study that employed a triangulation between quantitative and qualitative research approaches. This approach enables the researcher to collect and analyze both quantitative and qualitative data and the relationship between independent variable (employee turnover) and the dependent variable (Organizational Performance) of Bekas chemicals PLC.
The researcher was used both primary and secondary data sources. To estimate the determinant of employee’s turnover intention of Bekas chemicals PLC, the researcher was gathered data from corporate Manager, Department Manager, Head of sections, Forman, Support staff , Ex-employees and annual report.
The primary data were gathered by using adopted questionnaire from different studies such as Abdali (2011), Shah, et al., (2010) and modified by the researcher in order to relate it with the specific objective of the research [11]. Questionnaire were designed to gather data from employees of the Bekas chemicals PLC. In addition, researcher used structured interview to collect data from Corporate manager, Department manager and Ex- employee’s. The researcher decided to use questionnaire because, it will help him gather basic data from large number of respondents with less time, and interview to get the advantage of collecting detailed information from small number of respondents. Regarding the collection of secondary data, the researcher referred different reports.
The population of the study consist of 544 members from both Adama and Addis Ababa branch offices: of these total working forces of the organization: Top management =7(Managing Director 1, CEO 1, Corporate Managers 5), Middle management=26 ( Department Managers 12, Heads of sections 14), Front line management=13 (Forman=13), Support staff (475) working at Bekas chemicals PLC. The sample technique used for the study was both probability and non probability sampling technique. Hence, sample size was determind using by Taro Yamana’s simplified formula.
Where,
n = sample size N = population
e = standard error or precision rate. Calculating the sample size: n = 544/ [1+544*.052] = 231
Questionnaire was used to collect primary data from the respondents and the researcher used self-administered questionnaire for this study and semi-structured instruments to collect data from existing employees of the organization. Closed end and scaled stems were carefully applied to get all necessary information. Data was thematically categorized in order to as respondents easily understand and express their feelings, Likert scale was used which enables to understand respondents degree of agreement with each statement in the study.
The researcher was collected data personally using unstructured (non directive) interview issues related to employee turnover. Participants who were accessed through this interview were CEO, Corporate manager, Managing director and two department managers. In the same way a sample of ex-employees were accessed through this interview.
The reliability of the questionnaires items were tested on 26 pilot respondents to check on its internal consistency using Cronbach alpha result for all categories of the questionnaire. The result calculated through SPSS indicates that the value of Cronbach’s alpha equals to 0.889. After establishing reliability of the instrument, the validity of the instrument were reviewed through content validity based on randomly selected 20 pilot test. The calculated score measurement became 0.93 this means that the instrument was reliable. Content validity ratio(CVR) of the inistrument were checked based on 6 experts to check the clarity, relevancy and simplicity of the tool.
Quantitative data analysis was used to analyze data. Data collected from the field was analyzed and coded. Quantitative data collected was analyzed by the use of inferential statistics using Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) version 25 and presented through tables. Mean and standard deviation and percentages were used to present results. Correlation analysis was done to determine the relationship between all indipendant variables with dependant variable and regression. According to Cooper and Schindler (2014), a correlational research design is used to describe a phenomenon or features associated with a population and also to find out if there is a relationship among these different variables.
The present study results indicate that impact of employee turnover are significant predictors of organizational performance in Bekas chemicals PLC as shown in the regression analysis model. The regression analysis results are further supported by the correlation analysis results. The correlation analysis results indicate that there is a significant positive relationship between turnover variables (independent variables) and organizational performance [12-18].
|
|
|
DV |
PV |
EV |
OP |
|
DV |
Pearson Correlation |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
Sig. (2-tailed) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
N |
213 |
|
|
|
|
PV |
Pearson Correlation |
.771** |
1 |
|
|
|
|
Sig. (2-tailed) |
.000 |
|
|
|
|
|
N |
213 |
213 |
|
|
|
EV |
Pearson Correlation |
.578** |
.507** |
1 |
|
|
|
Sig. (2-tailed) |
.000 |
.000 |
|
|
|
|
N |
213 |
213 |
213 |
|
|
OP |
Pearson Correlation |
.731** |
.661** |
.707** |
1 |
|
|
Sig. (2-tailed) |
.000 |
.000 |
.000 |
|
|
|
N |
213 |
213 |
213 |
213 |
|
**. Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed). |
|||||
Source: Field survey data, (2020.)
The relationship among all the variables was found by using Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient. The correlation value r(213),0.731,p?0.01 shows that there is a strong relationship between demographic causes of employee turnover and organization performance, and the p-value shows that the relationship is significant. The same is true to psychological causes of employees turnover and economic causes of employee turnover and organization performance with r(213),0.661,p?0.01 and r(213),0.707,p?0.01 respectively, which shows that these two variables are strongly correlated with organization performance, also the p-value shows the relationship is significant.
Before regression analysis carried out the researcher have to take statistical test of Multi-co-linearity (VIF), linearity, Normality test, Auto correlation test.
Model Summaryb
|
Model |
R |
R Square |
Adjusted R Square |
Std. Error of the Estimate |
Durbin-Watson |
|
1 |
.888a |
.789 |
.786 |
.16717 |
.330 |
a. Predictors: (Constant), Aggregate Economic Variables, Aggregate Psychological Variables, Aggregate Demographic Variables
Source: Field survey data, (2020)
From the model summary above, it has realized that all the independent variables has a moderate relationship with organizational performance. The correlation value is 0.888, considered a moderate relationship because the value fall greater than 0.70 (Pallant, 2011). The value is also positive indicating that, when the independent variable increase dependent variable also increases and vice versa. The R² indicate that 78.9% (0.789) of organizations performance could be explained by the independent variables.
|
Model |
Unstandardized Coefficients |
Standardized Coefficients |
T |
Sig. |
Collinearity Statistics |
||
|
1 |
B |
Std. Error |
Beta |
|
|
Tolerance |
VIF |
|
(Constant) |
1.338 |
.252 |
|
6.101 |
.000 |
|
|
|
DV |
.423 |
.033 |
.893 |
12.787 |
.000 |
.150 |
6.677 |
|
PV |
-.367 |
.082 |
-.295 |
-4.460 |
.000 |
.177 |
5.650 |
|
EV |
.532 |
.061 |
.341 |
8.751 |
.000 |
.646 |
1.548 |
Source: Field survey data, (2020.) F(212,5) , p<0.01, R² = 0.789
As indicated in table 4.3 Unstandardized Coefficients B= .423 for Aggregate Demographic Variables. This means that when the other independent variables (psychological and economic variable) are held constant, a 1 degree improvement on demographic causes of employee turnover increases organizations performance by 42.3% . The result of Unstandardized Coefficients (B= -.367) for Aggregate Psychological Variables imply that a 1 degree improvement in causes of turnover can save the organizational performance from declining by 36.7%. Here, the result of finding supported the inverse relationship logic of organizational performance and employee’s turnover. The result of Unstandardized Coefficients for Aggregate economical Variables (B= .532) shows that a 1 degree/ unit/ improvement or change in economic causes of turnover increase/improve or change the organizational performance of Bekas chemicals plc by 53.2% .
The findings result were found that psychological variables (i.e. Job satisfaction and job security) was the dominant factor causing employees’ turnover showing turnover coefficient were negatively related to organizational performance.
The organizational performance has been related moderately and significantly to employee turnover as shown by beta coefficient of determination. This implies that voluntarily turnover were moderately and significantly related to organizational performance in Bekas Chemicals PLC, and there is no clear evidence that involuntary turnover has no significant relationship with organizational performance in specific period.
The impact of employees’ turnover leads to loss of the most competitive and experienced staff and this influences the organization to incur huge expenditure in recruitment and training of the new employees. The new employees’ exhibits low level of effectiveness and efficiency in the execution of the organization job task functions and this lowers the performance of the individual employees that in turn lowers the level of organization performance.
