Seamless Transition Strategies: A Comprehensive Checklist for Upgrading Time and Attendance Kronos Systems
Author(s): Karthikeyan Manikam
Abstract
Upgrading Time and Attendance systems is pivotal for organizational efficiency and workforce management. This article presents a detailed checklist aimed at ensuring a seamless transition during system upgrades. It encompasses pre-upgrade strategies such as establishing goals, understanding new features, and conducting a technical and risk assessment, alongside ensuring stakeholder communication and planning for training and support. During the upgrade, it underscores.
Introduction
Upgrading enterprise systems is a significant undertaking for any organization, and Kronos system upgrades are no exception. Given the critical nature of time and workforce management systems in efficient business operations, it is essential to approach the upgrade process with a thorough and methodical strategy. Moving from one version of Kronos to another is not just a technical task; it is an organizational project that requires meticulous planning and execution.
The key to a successful upgrade lies in preserving data integrity, minimizing disruption to operations, and facilitating a smooth transition for users to the enhanced system. This article provides a comprehensive checklist for upgrading Kronos systems. It is tailored to facilitate a systematic approach for each phase: pre-upgrade preparation, executing the upgrade, and critical post-upgrade activities. By following this checklist, organizations can achieve a seamless upgrade experience that enhances system capabilities and aligns with organizational goals and workforce expectations.
Pre-Upgrade Checklist Project Planning
Establish Upgrade Goals: Define the objectives you want to achieve with the upgrade, such as enhanced features, improved performance, better employee experience, and enhanced security.
Review Release Notes: Understand the changes, new features, and fixed issues in the new version. Download the release notes from the following link Workforce Management Release Notes
Process and Policy Evaluation: An upgrade event provides your organization and leadership team with an ideal opportunity to evaluate your existing processes and policies. Consider whether your current configuration is working to your satisfaction and what changes might be needed.
Upgrade Path Clarity: Confirm the upgrade path from your current version to the target version. You should have clear understanding of the steps, Process, requirements,
- Version Compatibility: Knowing which versions of Kronos you can directly upgrade to from your current version. Sometimes you can’t jump several versions ahead without intermediate steps.
- Sequential Steps: If the upgrade requires moving through intermediate versions before reaching the target version, you need a clear plan for each step.
- Pre-Requisites: Understanding any prerequisites that must be met before starting the This could include hardware requirements, database updates, or third-party software dependencies.
- Customization Retention: Ensuring that any customizations or integrations in the current system will be retained or appropriately modified to work with the new version.
- Testing Protocols: Knowing the testing protocols to follow after each upgrade step to ensure system integrity and functionally.
- Documentation: Having access to detailed documentation that outlines the upgrade process for your specific scenario.
- Support: Knowing how to access vendor support during the upgrade process in case of issues.
Technical Assessment
Complexity and Optimization Review
Prior to initiating the upgrade, it is crucial to thoroughly document the current configuration of Kronos and align this information with the ideal future state after the upgrade. This involves evaluating and validating Pay Rules, Work Rules, Pay Code Distribution, Shift Rules, and other relevant factors.
Additionally, it is important to identify any existing Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) that are currently being utilized. This step helps to uncover any workarounds being employed to address current challenges and enables the planning of appropriate resolutions during the upgrade process.
Fit/Gap Analysis: Validate the current system state and document any potential issues that might arise during the upgrade. This might consist of a Fit/Gap analysis showing where upgrade issues might arise
Configuration Path Decision: Decide on your migration path. You can opt for a straight migration, moving existing configurations as much as possible, or an optimized migration that considers your specific Workforce Management (WFM) processes and configures an optimized UKG Dimensions solution
1. System Health Check
Perform a system health check to identify any existing issues.
- Resource Utilization: Monitor the utilization levels of system resources, including CPU, memory, disk space, and network bandwidth, to identify any bottlenecks or instances of overutilization.
- Database Health: Examine the database for issues such as fragmentation, index performance, and ensure that maintenance tasks like backups and integrity checks are running as scheduled.
- Customizations and Integrations: Document any customizations or Work force integration mangers (WIM) integrations and ensure they are functioning correctly and are well-documented with their current run time.
- Compatibility Check: Ensure that your hardware and software meet the requirements of the new version.
- Database Backup: Take a complete backup of your current database and system configurations.
Risk Management
Risk Assessment: Identify potential risks associated with the upgrade. Some common risks that could occur during the Kronos upgrade as follows:
- Technical Risks: These include potential issues with the upgrade process itself, such as software bugs, compatibility issues, or unexpected system behavior. For instance, the upgrade might not go as smoothly as expected, leading to disruptions in the workforce management processes.
- Operational Risks: These risks involve potential disruptions to business operations during the upgrade process. For example, during a major system upgrade, Kronos may be offline, affecting the ability of employees to record their hours or supervisors to input employee times.
- Security Risks: Upgrading to a new version of Kronos could potentially expose the system to security vulnerabilities if not properly For instance, the Kronos ransomware attack in 2021 affected many organizations, causing disruptions in payroll processing and access to employee attendance records.
- Compliance Risks: These risks involve potential non- compliance with regulations or internal policies due to changes in the system. For instance, different versions of Kronos might use different modules with different rules, leading to inconsistencies in the employee experience3.
- Resource Risks: These involve potential issues with the availability or capability of resources needed for the For instance, there might be a lack of skilled resources to manage the upgrade process, or there might be insufficient hardware to support the new version.
- Change Management Risks: These risks involve potential issues with managing the change from one version to another. For instance, employees might resist the change, or there might be a lack of effective communication about the
- Rollback Plan: Develop a rollback plan in case the upgrade needs to be reversed.
- Define Rollback Criteria and Triggers: Before deploying a new system or a major update, you should define the criteria and triggers for rolling back to the previous version. These can include technical issues, such as bugs, errors, failures, or performance degradation, as well as business issues, such as user feedback, compliance, or revenue loss.
- Prepare a Rollback Plan: A rollback plan should outline the steps, roles, responsibilities, and dependencies for restoring the previous version of the system. It should also include contingency plans for handling any potential risks or complications during the rollback process. A rollback plan should be tested and validated before the deployment to ensure its feasibility and reliability.
- Prepare Necessary Resources: You should prepare the necessary resources for the rollback, such as backup data, configuration files, scripts, tools, and documentation. This will ensure that you have everything you need to restore the previous version of the system if the upgrade fails.
- Metadata Rollback: Identify any profiles, permission sets, and role changes during rollback, do an impact assessment, and restore changes You should also identify users modified with profiles, roles, permission sets, and rollback after impact only.
- Integration Rollback: Create a master copy of records from external systems based on records created or modified based on the date range. Have a reconciliation process to identify the impact and update records manually.
- Security Considerations: Do not ignore security and ensure records with the right access are restored. Have a plan for manual reconciliation.
- Operational Contingency Planning: Consider how the business will cope during any unexpected downtime. The criticality of processes should be assessed and factored into contingency plans together with any manual failover actions
Stakeholder Communication
Inform Stakeholders: Notify all stakeholders about the upcoming upgrade and its implications.
Downtime Notification: Communicate any expected downtime to users and stakeholders.
Training and Support Planning
Identify Training Needs: Determine if new training will be required for users or IT staff.
Support Team Briefing: Ensure the support team is prepared for potential post- upgrade issues.
During Upgrade Checklist System Downtime
Schedule Downtime: Perform the upgrade during off-peak hours to minimize impact.
Upgrade Execution:
Follow Upgrade Guide: Execute the upgrade steps as per Kronos’s documentation.
Monitor Upgrade Process: Closely monitor the upgrade process for any errors or warnings.
- Monitor System Performance: Keep an eye on the system’s performance during the upgrade. Any significant changes in performance could indicate a problem that needs to be adressed.
- Monitor for Errors: Be vigilant for any errors or issues that arise during the upgrade. This could include technical problems, bugs, or failures. If any issues arise, be prepared to adjust the schedule or implement contingency plans as needed.
- Monitor User Activity: During the upgrade, users who record their hours using a time clock can punch in and out, but the smart key functions at the time clocks
will not function. Users who typically timestamp at their computers should notify their supervisors of their in and out times, either by emailing at the beginning and end of their shift that day or by using another departmentally-approved procedure.
Testing
Functionality Testing: Test core functionalities to ensure they are working as expected.
- Testing the functionality of the application to generate the desired output on providing a certain input.
- Ensuring that all functionalities of the application are validated and verified.
Integration Testing: Verify that all integrations with other systems are intact.
- Testing the integration of different modules together.
- Testing the WIM interface.
- Testing the external integrations.
Performance Testing: Ensure the system performs well under typical loads.
- Observing response times when executing a high number of requests.
- Determining how the system behaves with a significant amount of data.
- Locating bottlenecks and measuring stability during peak traffic.
- Ensuring that the application meets performance requirements.
Post-Upgrade Checklist Validation
- Data Validation: Confirm that all data is accurate and intact post-upgrade.
- Audit Trails: Check audit trails and logs for any issues during the upgrade.
User Verification
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Have key users validate the system functionality.
- Collect User Feedback: Obtain feedback to identify any issues from a user perspective.
Issue Resolution
- Address Issues: Resolve any issues that were identified during testing and UAT.
- Update Documentation: Ensure all system documentation reflects the new version.
Training and Communication
- Conduct Training: Provide training on new features and
- Update Users: Communicate the completion of the upgrade and any relevant changes to all users.
Monitoring
- System Monitoring: Monitor the system for stability and performance issues.
- Support Availability: Ensure that support is readily available to handle any post- upgrade queries or issues.
Finalization
- Close Project: Once satisfied with the upgrade, formally close the upgrade project.
- Lessons Learned: Document lessons learned and best practices for future upgrades.
By following this checklist, you can aim for a seamless transition to the new version of Kronos, ensuring that the system continues to support your organization’s time and attendance needs effectively.
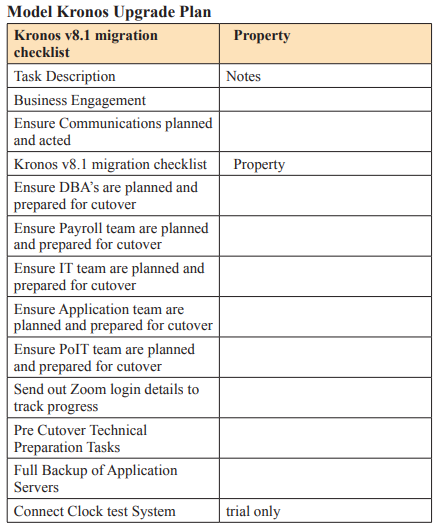
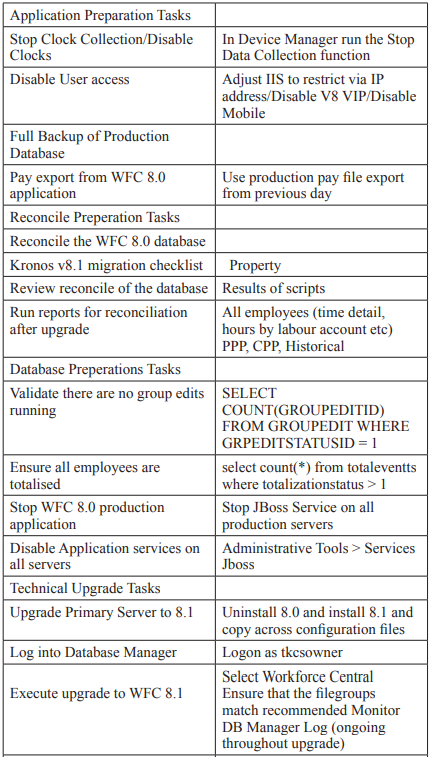
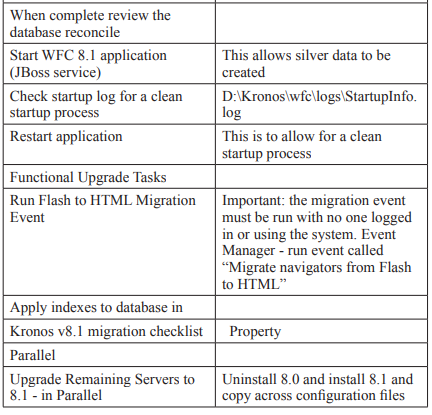
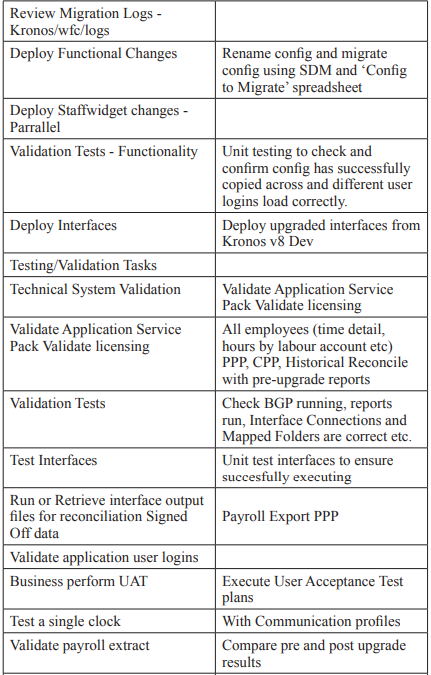
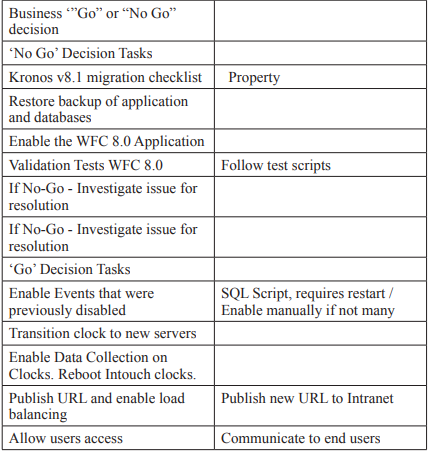
Conclusion
The upgrade of a Kronos system, when executed in alignment with a detailed and strategic plan, can significantly enhance the efficiency and functionality of workforce management within an organization. The outlined checklist serves as an essential guide, ensuring that no critical step is overlooked during the transition from one version to another. By meticulously following the pre- upgrade, during upgrade, and post- upgrade steps, organizations can mitigate risks, minimize downtime, and leverage new features to their fullest potential.
It is crucial to engage all stakeholders, assess the system’s readiness, manage risks, and provide adequate training and support throughout the upgrade process. While challenges are inherent in any system upgrade, a well-prepared approach, as encapsulated by the checklist provided, can transform these challenges into opportunities for improvement and innovation within the workforce management processes.
In essence, the upgrade process extends beyond mere technical implementation—it encapsulates a broader vision for process enhancement and operational excellence. As organizations look to the future, this holistic methodology not only ensures a robust and reliable upgrade but also sets a precedent for continuous improvement and adaptation in an ever-evolving technological landscape.
References
- HR data migration checklist and tips for implementation TechTarget https://www.techtarget.com/searchhrsoftware/tip/HR-data-migration-%20checklist-and-tips-for-implementation-success.
- Improv Flash Free Upgrade. HubSpot https://cdn2.hubspot.net/hubfs/42614/pdf_downloads/IMPROV_FlashFreeUpgrade.
- Kronos Upgrade Version 8.1.4. Timekeeping UCSB https://www.timekeeping.ucsb.edu/news/kronos-upgrade-version-814.
- The Kronos Ransomware Attack: What You Need to Know So Your Business Isn’t Next. Dark Reading https://darkreading.com/vulnerabilities-threats/the-kronos-ransomware-attack-what-you-need-to-know-so-your-business-isn-t-next.
- B DeSilva Best Practices for Workforce Management System LinkedIn https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/best-practices-workforce-management-system-upgrades-bryan-desilva/.
- Brian Myers (2022) UKG Dimensions Migration: What Customers Should Know. Healthcare IT Leaders https://healthcareitleaders.com/blog/ukg-workforce-central-wfc-end-of-life/.
- 4 Tips for Building a Business Case for Upgrading. UKG https://www.ukg.com/sites/default/files/legacy/kronos/resources/pdf/en/cv1036-usv3_4-%20tips-for-building-a-business-case-for-upgrading.pdf.
View PDF





