Author(s): Mahesh Deshpande
Project management stands at the precipice of a significant transformation driven by Generative AI (GenAI). This paper delves into the profound impact of GenAI on project managers, exploring how it reshapes roles, responsibilities, and the future of the field. We begin by outlining the evolution of AI, highlighting the emergence of GenAI and its ability to go beyond analysis and create novel content. GenAI will transform project management responsibilities from fully automated activities to a blend of assisted and augmented tasks, requiring collaboration and strategic application of this innovative technology. The paper explores the evolution of project management methodologies and the evolving skillset required of successful project managers in the age of AI and offers a "Project Manager's Guide to Thriving in the Generative AI Tsunami" by outlining the three pillars of the PMI Talent Triangle: Ways of Working, Power Skills, and Business Acumen. Each pillar is examined in detail, highlighting the role of GenAI in enhancing mastery and providing illustrative examples of AI-powered tools and frameworks. This paper equips project managers with the knowledge and tools to not only survive but thrive in the age of GenAI, ensuring their continued value and leadership in shaping successful projects.
Project management, like many industries, finds itself at the precipice of a paradigm shift driven by artificial intelligence (AI). Once relegated to the realm of science fiction, AI is now rapidly transforming every sector, weaving itself into the fabric of our work, lives, and even how we think. From groundbreaking healthcare applications to self-driving cars, AI's impact is undeniable. Coined in 1955, AI initially progressed slowly, its early milestones marked by victories in games like checkers and chess. However, the mid-2010s marked a turning point with the rise of deep learning, fueled by advancements in neural networks and processing power. This "new era" of AI capabilities culminated in the launch of OpenAI's ChatGPT in late 2022, displaying the power of generative AI to the public and pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
The transformative potential of generative AI extends far beyond a single industry, impacting every function and role, including project managers. Since the Agile Manifesto's publication in 2001, project management has undergone a significant evolution, transitioning from process-centric to principles-based methodologies. The emergence of generative AI tools presents exciting opportunities for automation within project management tasks, raising questions about the future of the role itself.
This paper delves into the profound impact of Generative AI on project managers, explores the impending transformation of the Project Management field, and equips project managers with the tools they need to adapt and thrive amidst this tsunami of change and continue as valuable contributors in the AI-powered future.
The democratization of AI began at the turn of the millennium, with pioneers laying the groundwork through statistical and machine learning techniques. These early efforts paved the way for applications like image recognition and basic natural language processing. By the mid-2010s, the emergence of deep learning, fueled by powerful GPUs and advancements in neural networks, ushered in a new era of AI capabilities. This era witnessed breakthroughs in computer vision, natural language understanding, and platforms like Google Translate and Apple's Siri brought AI's power to our daily lives [6]. Chatbots further revolutionized customer service.
Now, at the forefront of this revolution stands Generative AI (GenAI). While traditional AI excels at analyzing data, recognizing patterns, and making predictions, GenAI takes a leap forward by creatively crafting new content. Operating on neural network architectures like Generative Pre-trained Transformers (GPTs), GenAI can improvise on vast amounts of training data to create entirely new content. It possesses the remarkable ability to grasp context, semantics, and intricate language patterns based on massive text inputs.
GenAI's ability to generate novel outputs in six key formats - text, image, audio, video, code, and 3D specialized models - makesit a game-changer [1]. Analyzing existing use cases reveals five key value categories captured by GenAI: reducing operating costs, improving process efficiency, increasing revenue growth, accelerating innovation, and discovering new insights.

Figure 1: Value Captured from Gen AI Use Cases
This value captured spans from startups to large enterprises, highlighting the potential for disruptive change. GenAI is already impacting major functions across organizations.
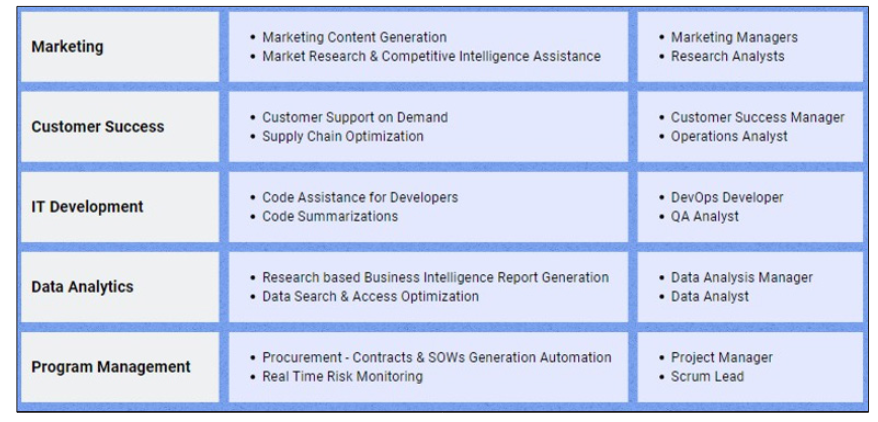
Figure 2: Gen AI's Impact on Various Functions within an Organization
GenAI's impact on various functions, including project management, does not imply a complete replacement of human roles. Instead, it will transform responsibilities and activities. The impact can be categorized along three dimensions:
Project management emerged as a distinct discipline after World War II with the US Navy's Polaris missile project, evolving from its roots in systems management [7]. However, the past few decades have witnessed a rapid acceleration in this evolution. Driven by the demands of faster product development and deployment, particularly in technology, the once-dominant predictive waterfall method proved inadequate.
In 2001, the Agile Manifesto offered a new paradigm for software development, spawning diverse frameworks and methodologies like Scaled Agile and Disciplined Agile that now extend to a wider range of projects. Recognizing the limitations of a one-size-fitsall approach, organizations increasingly adopt hybrid methods tailored to their unique needs.
This changing landscape has drastically reshaped the project manager's skillset. The latest edition (seventh) of PMI's PMBOK Guide, published in 2021, reflects this global shift from processdriven standards to a value-centric approach. Beyond traditional portfolio, program, and project management expertise, project managers now require a keen understanding of the value chain linking organizational strategy to business value [8]. The focus has shifted from outputs to outcomes, ensuring delivered projects demonstrably enhance stakeholder value [9]. While managing the "iron triangle" of scope, cost, and schedule remains crucial, today's project manager needs to excel in collaborative leadership and techno-functional domain skills [10].
Now, Generative AI enters the scene. Repetitive, low- cognitive tasks within project management are automated, forcing further refinement of existing knowledge and acquisition of new skillsets [10]. Project managers who embrace collaboration and leverage GenAI's power to enhance their effectiveness, creativity, and strategic decision- making are best positioned to thrive in this evolving landscape.
The constant influx of new GenAI tools and frameworks demands agility from project managers. To navigate this "tsunami of transformation" effectively, unlearning outdated skills and actively acquiring new ones is paramount. PMI's Talent Triangle offers a valuable framework for this professional development journey [13]. The Talent Triangle rests on three pillars: Ways of Working, Power Skills, and Business Acumen. Let us delve into the three pillars and how GenAI can reshape it.
Compare today's project management landscape to just seven years ago. Back then, expertise in managing scope, cost, schedule, quality, along with basic agile ceremonies and a couple of tools like JIRA, marked a good candidate. Today, an ever-expanding landscape of methodologies, frameworks, and tools requires adaptability.
The core of Mastering Multiple Ways of Working is the ability to orchestrate tasks and events towards successful project delivery. Instead of fixating on any single methodology, framework, or tool, project managers should become familiar with multiple options and select the most suitable approach for each project. Tool selection often depends on budget and organizational strategy, factors beyond a project manager's direct control. Rather than focusing on tool-specific outputs, prioritize adopting the best practices, techniques, and tools that enable successful project management regardless of the framework or methodology chosen.
Generative AI can be leveraged to automate, assist, and augment Ways of Working for both predictive and adaptive projects [11]. Here are some illustrative examples:
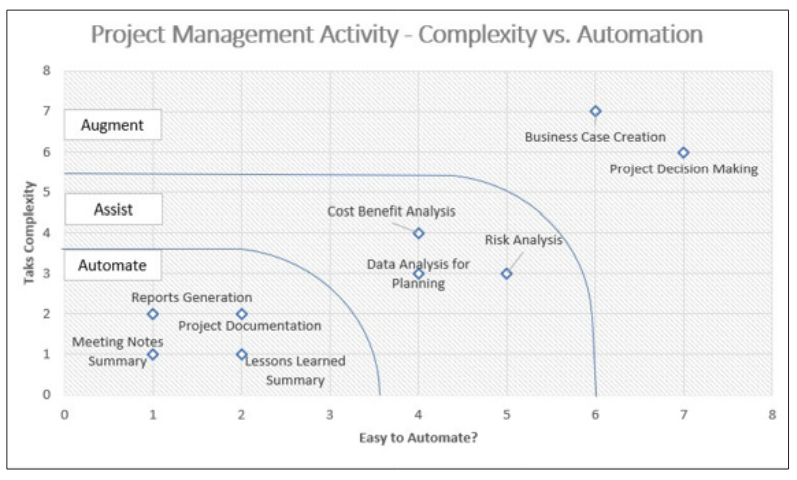
Figure 3: Project Management Activities: Complexities vs. Ease of Automation
By actively engaging with these evolving tools and cultivating mastery across multiple Ways of Working, project managers can position themselves as indispensable assets in the age of Generative AI [13]. Continuously learning, adapting, and leveraging the power of AI will be key to not only surviving but thriving amidst this transformative wave.
A 2023 PMI Pulse survey revealed four critical interpersonal skills project managers worldwide deem crucial for success [3]. Project Managers should envision these "power skills" in the context of project execution:
Project managers can function as guiding lights, ensuring project roadmaps align with organizational goals and industry trends.
Cultivating their inner alchemist, project managers can masterfully dissect problems using analytical thinking and logical reasoning.
Fostering discussions, mediating conflicts, and building trust become the hallmarks of skilled navigators who excel in bringing teams together.
Through empathetic listening, offering constructive feedback, and persuasively driving decisions, project managers become influential voices across various disciplines.
Developing a growth mindset is the cornerstone of acquiring these power skills. Consistent application throughout project engagements allows for continuous refinement.
Mastering Strategic Thinking involves delving into the organization's growth strategy, aligning programs with overall objectives, and actively seeking diverse perspectives on industry trends and forecasts can equip project managers with a forward-thinking vision. Problem Solving can be cultivated through brainstorming sessions with teams, experimenting with various approaches, analyzing data for iterative solutions, and documenting experiences through case studies, articles, or blogs offer valuable practice grounds for honing critical thinking skills. Improving Collaborative Leadership entails taking initiative by seeking out cross-functional projects, facilitating key planning discussions, and delegating effectively with clear expectations and support fosters leadership prowess. Mastering Cross-Functional Communication implies practicing cultivating empathy, offering constructive feedback with clarity, celebrating team achievements, and seeking mentorship pave the way for effective communication across boundaries.
Generative AI can be harnessed to amplify project managers' power skills and expression. Here are some useful AI tools:
By actively cultivating these power skills and utilizing AI-powered tools, project managers can become even more effective leaders, collaborators, and problem- solvers. Continuous learning and adaptation are key to thriving in the ever-evolving landscape of project management.
Organizations now seek project managers who transcend generic skillsets and possess strong business acumen. This enables them to collaborate effectively with technical and business teams, as well as executive leadership. Cultivating this acumen requires focused development in three key areas:
Project managers must become industry savants, possessing a deep understanding of industry trends, competitive landscapes, and regulations. This empowers them to solve problems effectively and make informed decisions.
Project managers need to be functional experts, proficient in utilizing tools, executing techniques, and managing processes to achieve project goals.
While not requiring deep technical expertise, project managers should possess a solid understanding of core technical concepts to facilitate collaboration with technical teams and make informed project decisions.
Developing business acumen necessitates awareness of the industry's specific niches. Each industry has unique nuances and standards, and lacking this knowledge can limit a project manager's influence. Engaging with executives and industry leaders on specific topics, along with actively learning about the company and industry (leveraging AI tools when appropriate), can bridge the domain knowledge gap. Understanding the organization's specific functions and how projects are managed within its unique context is crucial for functional skill development. Project managersshould explore frameworks like scenario analysis, competitive intelligence analysis, and design thinking to stand out as leaders and drive decisions based on sound reasoning. The key areas for developing Project Manager’s Technical competency includes:
Sharpening business acumen requires a research-oriented mindset. Project managers can leverage generative AI tools like ChatGPT, BARD, Copilot, Claude, LLAMA, and GitHub Copilot to accelerate their learning journey. However, unlocking the true potential of these tools lies in prompt engineering
Prompt engineering is the key to effectively leveraging these AI tools. It involves crafting precise prompts to optimize the performance of large language models (LLMs) that power these tools [4]. Project managers can utilize prompt engineering not only to hone their domain and power skills but also to augment LLMs with their own domain knowledge.
A good prompt typically consists of:
• Task or Instruction: The specific action you want the model
to perform.
• Context: External information to ensure the model performs
better.
• Input: The question you are seeking an answer or information
for.
• Output format: The desired format for the tool's response
(e.g., bullets, tables).
Here are some effective prompting frameworks:
• R-T-F: [Act as a Role, Create a Task, Show as Format]
Example: Act as an experienced Scrum Master, develop a
comprehensive Definition of Done to set a clear understanding
of work expectations & standards, summarize in bullets in less
than 200 words.
• B-A-B: [Explain Problem Before, State Outcome After, Ask
for the Bridge]
Example: We are nowhere on the SEO Ranking List, we would
like to be in top 10 SEO Rankings in our niche industry, develop a
detailed plan with all the measures we should take to reach top ten.
Example: Act as a content strategist, review the contents provided below regarding the target audience and their interests and priorities, generate a detailed content strategy plan that would help us become a thought leader in our niche consulting space.
By mastering these frameworks, project managers can leverage prompt engineering to design powerful prompts that unlock the true potential of generative AI tools like Bard and ChatGPT, honing their skills without compromising authenticity [5]. It is critical to ensure that organizational compliance policies are adhered to, while utilizing these tools.
Effective Prompt Engineering can help project managers develop robust and effective prompting techniques to hone their business acumen and thrive in the age of Generative AI. The key lies in balancing the power of AI with their own expertise and judgment to create authentic and valuable outcomes.
The emergence of Generative AI presents both challenges and opportunities for project managers. While automation may replace some repetitive tasks, it also opens doors for enhanced creativity, efficiency, and strategic decision- making. Embracing GenAI requires continuous learning and adaptation, honing both technical skills and interpersonal power skills. By mastering Ways of Working, cultivating Power Skills, and building Business Acumen, project managers can leverage GenAI to become even more effective leaders, collaborators, and problem-solvers. Tools like Miro, Canva, and Yoodli can amplify power skills, while AI- powered platforms like ChatGPT and BARD can accelerate learning and knowledge acquisition through effective prompt engineering. However, it is crucial to remember that AI is a tool, not a replacement for human expertise and judgment. By leveraging GenAI ethically and responsibly, project managers can navigate the "tsunami of transformation" and emerge as indispensable assets in the future of work. The key lies in embracing a growth mindset, actively seeking new knowledge and skills, and striking a balance between utilizing AI's power and maintaining human authenticity. Project managers who adapt to the Generative AI revolution will be well-positioned to lead projects to success, ensuring they continue to be indispensable contributors in shaping the future of work.
