Author(s): Vrushank Mistry
This comprehensive research paper investigates the paradigm shift in Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) control systems propelled by the transformative integration of the Internet of Things (IoT). In an era marked by the convergence of digital technologies, the infusion of IoT into HVAC systems heralds a new era of dynamic, interconnected control mechanisms. This study undertakes a thorough examination of the evolving landscape, shedding light on the profound advancements, discernible benefits, and nuanced challenges intrinsic to harnessing IoT for the augmentation of HVAC control systems. The journey begins by elucidating the fundamental shifts catalyzed by the assimilation of IoT in HVAC systems. The traditional boundaries of HVAC control are transcended as interconnected devices seamlessly communicate, fostering an environment where each component becomes an intelligent node in a networked ecosystem. Real-time data exchange becomes the bedrock, facilitating a level of monitoring and control hitherto unseen. The paper explores the intricacies of this interconnectedness, unveiling the potential for granular control and adaptability that IoT ushers into HVAC operations. A focal point of this research is the exploration of the tangible benefits that arise from this symbiosis of IoT and HVAC control. The paper meticulously examines how real-time monitoring empowers system operators with unprecedented insights into performance metrics, energy consumption patterns, and environmental conditions. Harnessing this wealth of data, IoT-equipped HVAC systems demonstrate an unparalleled capacity for adaptive control, responding dynamically to fluctuating demands and external variables. The consequential improvements in energy efficiency and resource utilization contribute not only to operational cost savings but also align with global sustainability objectives. However, in the pursuit of technological advancement, challenges inevitably emerge. This research critically evaluates the impediments and challenges inherent in the integration of IoT into HVAC control systems. Security concerns, data privacy issues, and the evolving landscape of technology standards are among the multifaceted challenges explored in depth. The paper endeavors to provide a nuanced understanding of these challenges, offering insights that can inform the development of robust and resilient IoT-enabled HVAC control systems.
In the realm of Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems, the conventional narrative revolves around the system functioning seamlessly until an abrupt halt, triggering a cascade of challenges involving expertise, tools, time, and effort for an effective diagnostic process. However, the landscape of HVAC controls is undergoing a transformative shift with the advent of Internet of Things (IoT) advancements, specifically in the domains of remote system monitoring, energy efficiency optimization, ongoing maintenance plans, and preventative maintenance strategies.
Traditionally, diagnosing HVAC issues necessitated physical presence, entailing labor-intensive processes and delayed responses. The integration of IoT has revolutionized this scenario, rendering remote system monitoring as simple as a glance at a smartphone app or website. This innovation not only caters to the needs of homeowners but also empowers property managers and HVAC contractors with real-time insights, facilitating rapid and accurate diagnostics.
IoT sensors, equipped to detect an array of variables such as pressure, vibration, flow, temperature, humidity, on/off cycles, and fault tolerance, have emerged as the vanguards of granular data acquisition. This depth of information provides technicians with unparalleled insights into the system’s health, laying the foundation for precise assessments and timely interventions. The choice of IoT protocols and standards shapes the nature and transmission of this data, offering a customizable approach to meet specific operational requirements.
The challenge of monitoring and optimizing energy efficiency, particularly in buildings with outdated HVAC systems, has long persisted. Traditional systems often lack the capability to provide real-time data, hindering the ability to make proactive adjustments. The IoT-driven solution introduces sensors into HVAC systems, enabling real-time data and fostering a proactive approach to energy management. This real-time monitoring not only optimizes climate control indoors but also positions HVAC systems as integral components of IoT-enabled smart grids.
Furthermore, the integration of IoT facilitates plans for ongoing maintenance, a cornerstone of HVAC companies’ revenue streams. The traditional model, requiring biannual on-site visits for HVAC maintenance, has evolved with IoT-enabled solutions. Remote monitoring and management of HVAC controls system enable HVAC companies to adopt a hardware-as-a-service (HAAS) model, ensuring proactive interventions and dispatching technicians only when necessary. Real-time data accessible through dashboards empowers customers with insights into energy consumption, usage patterns, and remote control capabilities, presenting new avenues for service agreements that contribute to enhanced monthly earnings.
In the realm of preventative maintenance, IoT sensors emerge as game-changers. The conventional reactive approach, where technicians respond to post-facto outage reports, contrasts with the condition-based approach offered by IoT sensors. Real-time data collection, cloud-based analysis, and condition monitoring enable HVAC contractors to proactively address issues before they escalate, often resolving problems remotely without physical site visits. This paradigm shift not only saves time, effort, and costs for HVAC contractors but also ensures uninterrupted service, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction.
For an IoT system to be deemed operational, its functionality hinges on the integration of the following four crucial components:
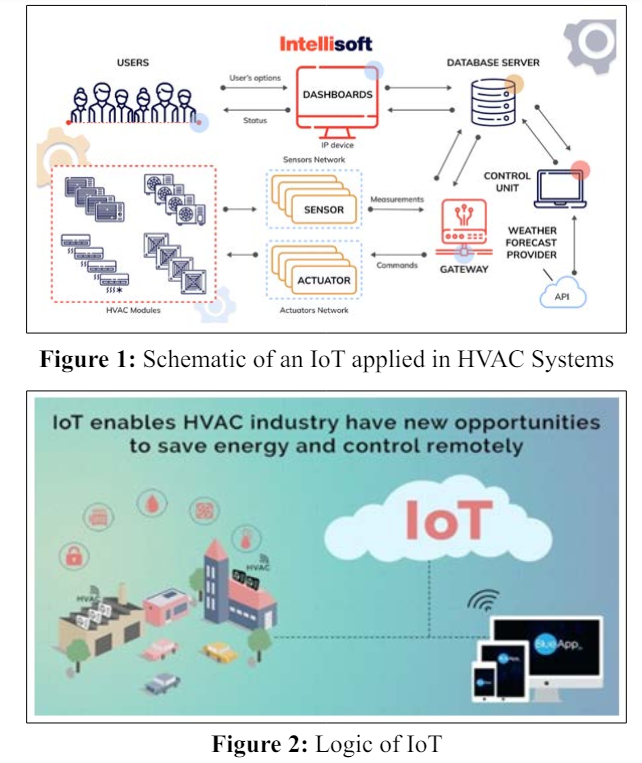
The integration of IoT in HVAC control systems involves the deployment of smart sensors, actuators, and communication technologies to create an interconnected network. This allows for real-time data collection, analysis, and responsive actions, transforming HVAC operations into dynamic and adaptive processes.
IoT-enabled sensors embedded in HVAC systems continuously monitor key parameters such as temperature, humidity, occupancy, and air quality. These sensors provide real-time data that can be utilized for precise control, allowing HVAC systems to dynamically respond to changing environmental conditions.
Cloud computing plays a pivotal role in the implementation of IoT in HVAC control systems. The collected data is transmitted to cloud-based platforms, where advanced analytics algorithms process the information. This data-driven approach enables predictive maintenance, energy optimization, and proactive decision-making for HVAC system performance.
The incorporation of IoT in HVAC control systems offers a multitude of advantages, revolutionizing the way these systems operate
Real-time monitoring and adaptive control facilitated by IoT contribute to significant energy savings and cost reductions. By adjusting HVAC parameters based on actual usage patterns, energy is utilized more efficiently, leading to reduced operational costs.
IoT-enabled HVAC systems can predict potential issues by analyzing performance data. This enables proactive maintenance, preventing costly breakdowns and reducing downtime. Predictive maintenance ensures that HVAC systems operate at peak efficiency, extending their lifespan.
The granular control provided by IoT allows HVAC systems to tailor environmental conditions to individual preferences. Occupants experience a higher level of comfort as the system adapts to their needs, leading to increased satisfaction and productivity.
While the benefits of integrating IoT in HVAC control systems are evident, challenges and considerations must be addressed for successful implementation
The interconnected nature of IoT raises concerns about data security and privacy. Protecting sensitive information transmitted between devices and cloud platforms is crucial to prevent unauthorized access and potential breaches.
The lack of standardized protocols for IoT devices in HVAC systems can hinder interoperability. Industry-wide standardization efforts are essential to ensure seamless integration and compatibility among different components and systems.
Typically, the components constituting the HVAC system include:
HVAC Sensors: Comprising sensors for temperature, motion, light, and various other environmental factors.
Gateway Infrastructure: Facilitating bidirectional communication between devices and the gateway, ensuring the seamless flow of data into and out of the smart HVAC system
HVAC Program: Responsible for collecting data from diverse sensors, conducting necessary analyses, and subsequently uploading the information to the cloud for further exploration.
Wireless Sensor Network: Transmitting information both to the cloud and the gateway, ensuring efficient communication across the HVAC ecosystem.
Cloud Analytics Platform: Serving as the central hub for data processing, offering functionalities such as filtering, examination, and sharing with other systems as needed.
Actuation Mechanism: A device or mechanism that translates electrical input from sensors into physical motion, executing actions based on the received data.
Learning Algorithms: Leveraging database data to enhance energy optimization, facilitate remote HVAC system control, and contribute to preventative maintenance. Additionally, system managers receive real-time notifications about errors, alerts, and events directly on their mobile devices.
In essence, entrusting the control and monitoring functions to an automated system eliminates the risk of resource overuse, positively impacting energy consumption efficiency
The advantages that an average household can enjoy when opting to automate HVAC systems.
The term “quality‘ refers to the composition of the home atmosphere, encompassing purity and oxygen saturation. A smart home-controlled ventilation system activates based on preprogrammed scenarios or readings from carbon dioxide level sensors. For instance, special indicators can be installed in rooms to detect tobacco smoke. Automation, considering various factors, independently determines the required ventilation, whether it involves turning on the hood or opening windows within specified temperature limits
HVAC components are prominent consumers of household energy. To save money and contribute to environmental protection, automation of heating, air conditioning, and ventilation can reduce energy costs by approximately one-third. The principle is straightforward: unoccupied rooms are not heated or cooled, preventing scenarios like unnecessary energy consumption in an empty house.
Adjusting temperature alone cannot ensure comfort in a humid room. High humidity not only affects occupants’ health but also harms wooden furniture and decorative elements like parquet. Smart air conditioning control maintains optimal humidity levels of 40-60%, considering external conditions such as wet rainy weather or dry air due to heating equipment in winter.
Intelligent automation distinguishes between heating requirements in corridors versus living rooms, optimizing energy usage. Radiators are activated shortly before occupants return, and scenarios can be time-dependent or influenced by external weather conditions, utilizing light sensors, schedules, or external weather stations for effective control.

The examination of IoT’s integration into HVAC control systems has yielded several noteworthy findings. Firstly, the real-time monitoring capabilities provided by IoT have proven instrumental in enhancing system diagnostics and fault detection. The continuous stream of data from sensors allows for proactive decision-making, mitigating potential issues before they escalate. Additionally, the utilization of learning algorithms has showcased a remarkable improvement in energy optimization, leading to more efficient HVAC operations.
The significance of IoT in HVAC control systems cannot be overstated. The seamless integration of IoT technologies has transformed traditional HVAC systems into intelligent, adaptive, and highly responsive entities. By connecting sensors, data processing units, and user interfaces, IoT empowers HVAC systems to operate with unprecedented efficiency and effectiveness. The ability to remotely monitor, analyze, and control HVAC systems represents a paradigm shift in building automation, offering a level of sophistication unattainable with conventional approaches.
One of the paramount advantages brought forth by IoT in HVAC systems is the substantial increase in energy efficiency. The continuous monitoring of environmental parameters, coupled with learning algorithms, facilitates precise control over heating, ventilation, and air conditioning processes. This precision translates to reduced energy consumption, resulting in tangible cost savings and a diminished environmental footprint. The potential for sustainability is further emphasized as IoT-enabled HVAC systems seamlessly integrate with smart grids, contributing to the broader goal of creating eco-friendly and energy-efficient built environments.
Recommendations for Organizations Considering IoT Integration: Integrating IoT into HVAC systems represents a transformative step for organizations. To ensure a seamless transition and optimal outcomes, it is imperative to consider the following recommendations:
As HVAC systems become increasingly interconnected through IoT, organizations must prioritize cybersecurity to safeguard against potential threats. Key considerations include:
Before embarking on IoT integration in HVAC systems, organizations should conduct a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis and engage in thoughtful long-term planning:
