Author(s): Venkata Tadi
The rapid evolution of cloud computing has opened new horizons for businesses of all sizes, with Amazon Web Services (AWS) leading the charge as a premier cloud service provider. This study delves into the unique challenges and opportunities faced by small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in maximizing the benefits of AWS to enhance operational efficiency and stimulate innovation. Through a comprehensive analysis of AWS's vast array of services, the research identifies key strategies and best practices tailored specifically for SMEs. These strategies encompass optimizing resource allocation, ensuring cost-effective scalability, and leveraging advanced AWS features to foster a culture of innovation. Additionally, the study provides practical insights into overcoming common obstacles SMEs encounter during cloud adoption and integration. By presenting detailed case studies and expert recommendations, this research aims to serve as an invaluable guide for SMEs seeking to harness the full potential of AWS, ultimately driving growth and competitiveness in an increasingly digital landscape.
Cloud computing represents a significant technological evolution in how computing resources are delivered and managed. Traditionally, businesses relied on on-premises data centers with substantial investments in hardware, software, and skilled personnel to manage their IT infrastructure. Cloud computing, however, shifts this paradigm by providing scalable, on-demand access to computing resources over the internet. This model not only reduces the need for upfront capital expenditures but also offers unparalleled flexibility and scalability.
Amazon Web Services (AWS), a subsidiary of Amazon, stands out as a leading provider of cloud computing services. Launched in 2006, AWS has grown to dominate the cloud market by offering a broad array of services that cater to diverse business needs. AWS's extensive portfolio includes computing power, storage options, networking capabilities, databases, analytics, machine learning, artificial intelligence, Internet of Things (IoT), security, and application development services.
One of the primary attractions of AWS is its Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) model, which allows businesses to rent virtual servers and storage. This model provides a pay-as-you-go pricing structure, which means organizations only pay for the resources they use. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for businesses with fluctuating or unpredictable workloads.
Moreover, AWS's Platform as a Service (PaaS) offerings, such as AWS Elastic Beanstalk, simplify the process of deploying and managing applications. These services abstract much of the underlying infrastructure management, allowing developers to focus more on coding and less on infrastructure logistics.
AWS also excels in providing Software as a Service (SaaS) solutions, enabling businesses to access software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. These services include AWS Marketplace, which offers a variety of third-party software solutions that can be seamlessly integrated with other AWS services.
The global reach of AWS is another critical advantage. AWS operates in numerous geographic regions worldwide, ensuring low-latency access to services and compliance with local data residency requirements. This extensive network of data centers also provides robust redundancy and disaster recovery capabilities, enhancing the reliability and availability of services.
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are pivotal to economic growth, often characterized by their agility and innovation. However, SMEs face unique challenges that can impede their growth, such as limited financial resources, a lack of technical expertise, and difficulties in scaling operations. Cloud computing, particularly through providers like AWS, offers solutions that address these challenges and can significantly enhance the operational efficiency and innovation potential of SMEs.
One of the most compelling benefits of cloud computing for SMEs is cost efficiency. Traditional IT infrastructure requires significant capital expenditure for hardware, software, and skilled personnel. Cloud computing, on the other hand, operates on an operational expenditure model, where businesses only pay for the resources they consume. This model reduces the need for large upfront investments and allows SMEs to allocate their financial resources more effectively.
Scalability is another critical advantage. SMEs often experience varying levels of demand, and traditional infrastructure can struggle to keep pace. Cloud computing provides the ability to scale resources up or down based on demand, ensuring that businesses can respond quickly to changes in the market without the need for significant infrastructure changes.
Additionally, cloud computing offers enhanced accessibility and collaboration. With cloud-based solutions, employees can access data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection, fostering remote work and collaboration. This capability is particularly valuable in today’s globalized and often decentralized business environment.
Security and compliance are also crucial considerations for SMEs. While managing security in traditional IT environments can be complex and resource-intensive, cloud service providers like AWS invest heavily in security technologies and practices. AWS offers a range of security features, including encryption, identity and access management, and compliance certifications, which can help SMEs protect their data and comply with industry regulations.
Cloud computing also empowers SMEs to leverage advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) without the need for specialized in-house expertise. AWS provides services like Amazon SageMaker, which simplifies the process of building, training, and deploying machine learning models. By accessing these advanced technologies, SMEs can drive innovation, improve decision-making, and create new products and services.
The primary objective of this literature review is to explore how small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) can maximize the benefits of Amazon Web Services (AWS) to enhance operational efficiency and drive innovation. This review will identify key strategies and best practices that are particularly effective for SMEs, addressing the unique challenges they face in cloud adoption and utilization.
To achieve this objective, the literature review will cover several key areas:
This section will examine the specific advantages that AWS offers to SMEs, such as cost efficiency, scalability, enhanced security, and access to advanced technologies. The goal is to understand how these benefits can be leveraged to improve business operations and competitive positioning.
Despite the numerous benefits, SMEs often encounter challenges when adopting cloud technologies. This section will explore common obstacles such as financial constraints, skill gaps, integration with legacy systems, and data security concerns. Understanding these challenges is crucial for developing effective strategies to overcome them.
Strategies and Best Practices for Effective AWS Utilization This section will identify and analyze strategies that SMEs can use to optimize their use of AWS. Topics will include resource allocation, cost management, leveraging AWS support and training programs, and implementing best practices for security and compliance.
Operational efficiency is a key driver of success for SMEs. This section will explore how AWS can help SMEs streamline their operations through automation, managed services, and performance management tools.
Innovation is essential for growth and competitiveness. This section will examine how SMEs can use AWS to foster a culture of innovation, encouraging experimentation, and integrating advanced technologies such as AI, ML, and IoT.
One of the paramount benefits of Amazon Web Services (AWS) for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) is its scalability and flexibility. Traditional IT infrastructure often requires significant upfront investments in hardware and software, which can be a considerable burden for SMEs with limited financial resources. Moreover, these traditional systems can be inflexible, making it difficult to scale operations in response to changing business needs.
AWS addresses these challenges by offering a scalable, flexible cloud infrastructure that can be easily adjusted to meet the evolving demands of a business. Scalability in the context of AWS refers to the ability to dynamically adjust the computing resources available to a business. This means that an SME can increase its capacity during periods of high demand and reduce it during slower periods, thus optimizing resource utilization and minimizing costs. This elasticity is particularly beneficial for SMEs that experience seasonal fluctuations or sudden spikes in demand [1].
AWS’s flexibility is further demonstrated through its vast array of services that can be tailored to meet specific business requirements. For instance, AWS offers various storage solutions, such as Amazon S3 for object storage and Amazon EBS for block storage, which can be selected based on the specific needs of the application or workload. Additionally, services like AWS Lambda allow businesses to run code without provisioning or managing servers, providing further flexibility and cost savings.
Sultan emphasizes that the cloud's inherent scalability and flexibility enable educational institutions to efficiently manage their resources and scale their operations as needed. This concept is equally applicable to SMEs, which can benefit from the ability to rapidly scale their IT infrastructure without the need for significant capital expenditures [1].
Cost efficiency is another critical advantage of AWS for SMEs. Traditional IT infrastructure requires substantial investments in hardware, software, and skilled personnel to manage and maintain the systems. These capital expenditures can be prohibitive for SMEs, which often operate with limited budgets. In contrast, AWS operates on a pay-as-you-go pricing model, where businesses only pay for the resources, they consume. This operational expenditure model reduces the need for large upfront investments and allows SMEs to better manage their cash flow.
Ercan highlights the cost benefits of cloud computing, noting that it enables organizations to avoid the significant expenses associated with purchasing and maintaining physical hardware. This shift from capital expenditure to operational expenditure is particularly advantageous for SMEs, as it allows them to allocate their financial resources more effectively and invest in other areas of their business [2].
AWS also offers various pricing models and tools to help businesses optimize their costs. For example, the Reserved Instances pricing model allows SMEs to reserve instances for a one- or three-year term, providing significant discounts compared to on-demand pricing. Additionally, AWS Cost Explorer and AWS Trusted Advisor offer insights and recommendations on how to optimize resource usage and reduce costs.
Senyo et al. discuss the importance of cost efficiency in cloud computing adoption, noting that the ability to reduce costs while maintaining or improving service quality is a key driver for businesses moving to the cloud. For SMEs, the cost savings associated with AWS can be a significant factor in their decision to adopt cloud computing [3].
Security and compliance are critical concerns for any business, but they can be particularly challenging for SMEs that may lack the resources to implement robust security measures. AWS addresses these challenges by providing a comprehensive suite of security features and compliance certifications that help protect data and ensure regulatory compliance.
AWS’s security framework includes features such as encryption, identity and access management, and network security. For example, AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) allows businesses to control access to resources and set permissions based on roles and policies. This granular level of control helps ensure that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive data and systems.
Sultan underscores the importance of security in cloud computing, noting that cloud providers like AWS invest heavily in advanced security technologies and practices to protect their customers' data. This investment in security is often beyond the capabilities of SMEs, making AWS an attractive option for businesses looking to enhance their security posture [1].
Compliance is another area where AWS excels. AWS offers a range of compliance certifications and attestations, including ISO 27001, SOC 1/2/3, and HIPAA. These certifications demonstrate that AWS meets stringent security and privacy standards, which can help SMEs achieve compliance with industry regulations. Senyo et al. highlight the importance of compliance in cloud computing, noting that businesses must ensure that their cloud provider adheres to relevant regulatory requirements to avoid potential legal and financial penalties [3].
One of the most significant benefits of AWS for SMEs is the access it provides to advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT). These technologies have the potential to drive innovation and create new business opportunities, but they often require substantial investments in hardware, software, and expertise that are beyond the reach of many SMEs.
AWS democratizes access to these advanced technologies by offering a range of services that make it easier for businesses to experiment with and implement AI, ML, and IoT solutions. For instance, Amazon SageMaker is a fully managed service that allows businesses to build, train, and deploy machine learning models at scale. This service simplifies the complex process of machine learning, making it more accessible to businesses with limited expertise in the field.
Ercan discusses the transformative potential of cloud computing in education, highlighting how access to advanced technologies can enhance teaching and learning outcomes. Similarly, SMEs can leverage AWS's advanced technologies to improve their operations, develop new products and services, and gain a competitive edge [2].
Moreover, AWS IoT Core enables businesses to connect IoT devices to the cloud and manage them securely at scale. This capability allows SMEs to collect and analyze data from connected devices, leading to improved decision-making and operational efficiency. Sultan notes that the ability to integrate and leverage advanced technologies is a key driver of cloud computing adoption, as it enables organizations to innovate and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market [1].
Financial constraints are one of the primary challenges that small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) face when adopting Amazon Web Services (AWS). While AWS offers a pay-as-you-go pricing model, which can be more cost-effective than traditional IT infrastructure, the initial costs of migration, training, and potential hidden expenses can still be significant hurdles for SMEs.
El-Gazzar highlights that one of the major issues in cloud computing adoption is the high initial investment required for transitioning to the cloud [4]. This includes costs associated with migrating existing data and applications, which can be both time- consuming and expensive. Additionally, there may be costs related to training staff to use the new system effectively, which can add to the financial burden.
Moreover, SMEs often have limited budgets and must carefully allocate their financial resources. The operational costs of running services on AWS can also accumulate over time, especially if the resources are not optimized. This financial unpredictability can be daunting for SMEs that require consistent and manageable expenses to maintain their operations smoothly.
Chang et al. discusses the economic challenges of cloud adoption, emphasizing the need for a well-structured financial strategy to manage these costs [5]. They suggest that businesses must conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis to understand the long- term financial implications of adopting cloud services like AWS. This includes considering the potential savings from reduced hardware and maintenance costs against the operational expenses of cloud services.
To mitigate these financial constraints, SMEs can take advantage of AWS's cost management tools, such as AWS Cost Explorer and AWS Budgets. These tools help businesses monitor their usage and spending, allowing them to make informed decisions about resource allocation and identify areas where costs can be reduced. Additionally, leveraging Reserved Instances and Savings Plans can provide significant discounts for long-term usage, making the financial management of AWS resources more predictable and affordable.
Another significant challenge for SMEs adopting AWS is the skill gap and the need for training. Cloud computing requires a different set of skills compared to traditional IT infrastructure, and many SMEs may not have personnel with the necessary expertise to manage AWS environments effectively.
El-Gazzar points out that the lack of skilled personnel is a critical barrier to cloud adoption [4]. This is particularly true for SMEs, which may not have the resources to hire or train staff with the requisite cloud computing skills. The complexity of AWS services, ranging from basic infrastructure management to advanced services like machine learning and data analytics, requires specialized knowledge that may not be readily available within the organization.
Chang et al. emphasizes the importance of organizational readiness and the need for comprehensive training programs to bridge this skill gap [5]. They suggest that businesses need to invest in training and development programs to equip their employees with the necessary skills to manage and optimize cloud resources. This includes not only technical training but also understanding the strategic implications of cloud adoption.
AWS provides a range of training and certification programs designed to help businesses develop the skills needed to use their services effectively. These programs include online courses, classroom training, and certification exams that cover various aspects of AWS, from foundational knowledge to advanced technical skills. By investing in these training programs, SMEs can build a knowledgeable team capable of managing their AWS environments efficiently.
Furthermore, SMEs can leverage AWS’s extensive documentation, whitepapers, and online forums to enhance their understanding of AWS services. Participating in AWS user groups and community events can also provide valuable networking opportunities and insights from other businesses that have successfully adopted AWS.
Integrating AWS with existing legacy systems presents another significant challenge for SMEs. Many businesses have invested heavily in their current IT infrastructure, and transitioning to the cloud requires careful planning and execution to avoid disruptions to their operations.
Khajeh-Hosseini et al. discuss the complexities involved in migrating enterprise IT systems to Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) [6]. They highlight the technical challenges and the need for thorough planning to ensure a smooth transition. For SMEs, these challenges can be even more daunting due to limited technical expertise and resources.
One of the key issues in integrating AWS with legacy systems is data migration. Moving large volumes of data from on-premises systems to the cloud can be time-consuming and risky, with potential for data loss or corruption during the transfer process. Additionally, there may be compatibility issues between existing applications and AWS services, requiring modifications or even complete redevelopment of certain applications.
Chang et al. highlights the importance of a phased approach to migration, where businesses gradually transition their systems to the cloud while maintaining operational continuity [5]. This approach allows SMEs to test and validate the new environment before fully committing to the transition, reducing the risk of disruptions.
To address these integration challenges, AWS offers various tools and services designed to facilitate data migration and integration. AWS Migration Hub provides a central location for tracking the progress of application migrations across multiple AWS and partner solutions. AWS Database Migration Service and AWS Snowball are also valuable tools that help in efficiently transferring data to AWS, ensuring minimal downtime and disruption.
Moreover, employing hybrid cloud architectures can provide a transitional solution, allowing SMEs to integrate their on-premises infrastructure with AWS. This enables businesses to gradually move their workloads to the cloud while still leveraging their existing investments in legacy systems.
Data security and privacy are paramount concerns for any business considering cloud adoption, and SMEs are no exception. Ensuring the security of sensitive data and maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements can be challenging when moving to a cloud environment like AWS.
El-Gazzar identifies security and privacy concerns as significant barriers to cloud adoption [4]. These concerns are heightened for SMEs, which may lack the expertise and resources to implement robust security measures. The potential risks include unauthorized access, data breaches, and loss of control over sensitive information.
Chang et al. discusses the importance of addressing security and compliance issues when adopting cloud services [5]. They emphasize the need for businesses to understand the shared responsibility model of cloud security, where the cloud provider (AWS) is responsible for the security of the cloud infrastructure, and the customer is responsible for securing their data and applications within the cloud.
AWS offers a comprehensive set of security features and compliance certifications to help businesses protect their data. These include encryption, identity and access management, network security, and monitoring and logging tools. AWS's compliance certifications, such as ISO 27001, SOC 1/2/3, and HIPAA, demonstrate its commitment to maintaining high-security standards.
Khajeh-Hosseini et al. highlight the importance of implementing best practices for cloud security, such as using multi-factor authentication, regularly updating security policies, and conducting regular security assessments [6]. For SMEs, adopting these best practices can significantly enhance their security posture and ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
Optimizing resource allocation is critical for small and medium- sized enterprises (SMEs) to maximize the benefits of AWS. Effective resource allocation ensures that businesses are not over- provisioning or under-provisioning their resources, which can lead to either unnecessary costs or performance bottlenecks. The dynamic nature of cloud computing requires a strategic approach to resource management to fully leverage AWS's capabilities.
One of the primary strategies for optimizing resource allocation is the use of AWS Auto Scaling. This service allows businesses to automatically adjust the number of EC2 instances based on demand. By setting up scaling policies, SMEs can ensure that they have the right number of resources at any given time, which helps in maintaining performance while minimizing costs. Marston et al. emphasize the importance of automated scaling in managing cloud resources efficiently, noting that it helps businesses respond to workload changes in real time without manual intervention [7].
Another key practice is right-sizing resources. This involves analyzing the usage patterns of various AWS services and adjusting the resource configurations accordingly. For instance, if certain instances are consistently underutilized, they can be resized to smaller instance types, or if they are overutilized, they can be scaled up to larger instances. AWS provides tools like AWS Trusted Advisor and Cost Explorer, which offer insights and recommendations on resource optimization. These tools can help SMEs identify underutilized resources and optimize their cloud infrastructure.
Sriram and Khajeh-Hosseini highlight the role of continuous monitoring and performance management in optimizing cloud resources [8]. By leveraging AWS CloudWatch, SMEs can set up alarms and dashboards to monitor the performance of their applications and infrastructure. This continuous monitoring enables proactive management of resources, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
Furthermore, implementing Infrastructure as Code (IaC) using tools like AWS CloudFormation and Terraform allows for consistent and repeatable resource allocation. IaC enables businesses to define their infrastructure using code, which can be version-controlled and automated. This approach not only reduces the risk of human error but also enhances the scalability and manageability of cloud resources.
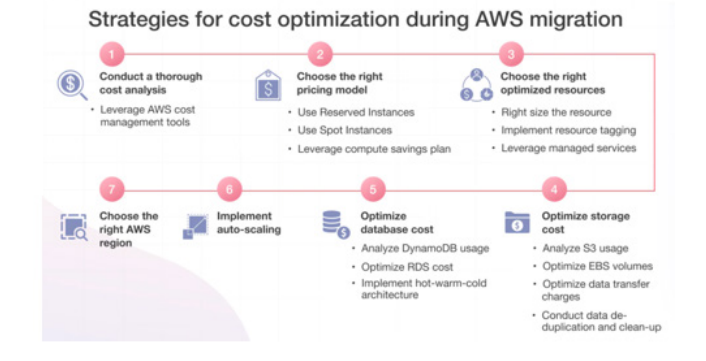
Cost management and optimization are vital for SMEs to ensure that their cloud spending aligns with their budget constraints and business goals. While AWS offers a pay-as-you-go pricing model, without proper cost management, expenses can quickly escalate, leading to budget overruns.
Marston et al. discuss the economic implications of cloud computing and emphasize the need for strategic cost management to maximize the return on investment [7]. One effective strategy is to take advantage of AWS's various pricing models, such as Reserved Instances and Savings Plans. Reserved Instances offer significant discounts for long-term commitments, while Savings Plans provide flexible pricing options based on committed usage. By committing to these plans, SMEs can achieve substantial cost savings compared to on-demand pricing.
Another important practice is implementing cost allocation tags. AWS allows businesses to tag their resources with custom metadata, which can be used to categorize and track costs across different departments, projects, or cost centers. This granular visibility into spending helps SMEs understand where their money is going and identify areas where costs can be reduced.
AWS Cost Explorer and AWS Budgets are essential tools for cost management. Cost Explorer provides detailed insights into spending patterns, allowing businesses to analyze their costs over time and forecast future expenses. AWS Budgets enable businesses to set custom cost and usage budgets, with alerts and notifications when spending exceeds predefined thresholds. These tools empower SMEs to maintain control over their cloud expenses and avoid unexpected costs.
Sultan highlights the potential of cloud technologies in transforming business operations but also warns about the challenges of managing costs effectively [9]. To address these challenges, SMEs should implement cost optimization best practices, such as terminating unused resources, scheduling instances to shut down during non-peak hours, and utilizing Spot Instances for non-critical workloads. Spot Instances offer significant discounts compared to on-demand prices, making them an attractive option for cost-conscious businesses.
Leveraging AWS Support and Training Programs Leveraging AWS support and training programs is crucial for SMEs to maximize their cloud investment and ensure successful adoption and utilization of AWS services. These programs provide the necessary resources and expertise to help businesses navigate the complexities of cloud computing.
AWS offers a range of support plans tailored to different business needs. The Basic Support plan provides access to AWS's extensive documentation and whitepapers, while the Developer, Business, and Enterprise Support plans offer varying levels of technical support and guidance. The Enterprise Support plan, for instance, includes a dedicated Technical Account Manager (TAM) who works closely with the business to provide strategic guidance and proactive support. Marston et al. note that having access to expert support is critical for businesses to resolve issues quickly and effectively, minimizing downtime and ensuring smooth operations [7].
Training and certification programs are also essential for building the necessary skills to manage and optimize AWS environments. AWS provides a comprehensive suite of training resources, including online courses, instructor-led training, and certification exams. These programs cover a wide range of topics, from foundational cloud concepts to advanced technical skills. Sriram and Khajeh-Hosseini emphasize the importance of continuous learning and skill development in keeping up with the rapidly evolving cloud landscape [8].
AWS certifications, such as the AWS Certified Solutions Architect and AWS Certified DevOps Engineer, validate the expertise of individuals and help businesses build a competent team capable of leveraging AWS to its fullest potential. Sultan highlights that well-trained personnel are essential for effectively managing cloud resources and driving business transformation [9].
Additionally, AWS offers various programs and resources to support startups and SMEs. The AWS Activate program, for example, provides startups with credits, training, and support to help them get started on AWS. This program is designed to reduce the financial barriers to cloud adoption and provide startups with the resources they need to succeed.
AWS Partner Network (APN) is another valuable resource for SMEs. By partnering with AWS-certified service providers, businesses can access specialized expertise and services to support their cloud initiatives. These partners can assist with everything from migration and implementation to ongoing management and optimization, helping SMEs achieve their cloud goals more efficiently.
Automation and DevOps practices are essential for enhancing operational efficiency in the cloud. By leveraging these practices, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) can streamline their workflows, reduce manual intervention, and accelerate the deployment of applications and services.
DevOps, a combination of development and operations, emphasizes collaboration between software developers and IT operations to improve the speed and quality of software deployment. AWS provides a range of tools and services that support DevOps practices, enabling SMEs to automate various aspects of their development and operational processes.
Armbrust et al. highlight the transformative potential of cloud computing, noting that automation is a key driver of efficiency in cloud environments [10]. AWS services like AWS CodePipeline, AWS CodeBuild, and AWS CodeDeploy allow businesses to automate their continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines. These services enable developers to build, test, and deploy code automatically, reducing the time and effort required to release new features and updates.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) is another critical aspect of automation in the cloud. IaC allows businesses to manage and provision their infrastructure using code, which can be version- controlled and automated. AWS CloudFormation and AWS CDK (Cloud Development Kit) are powerful tools that facilitate IaC, enabling SMEs to define their infrastructure as code and deploy it consistently across multiple environments. This approach not only reduces the risk of configuration errors but also ensures that infrastructure changes are documented and repeatable.
Dillon et al. discusses the challenges and benefits of cloud computing, emphasizing that automation is crucial for managing complex cloud environments efficiently [11]. By automating routine tasks such as scaling, backups, and patch management, SMEs can free up their IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives. AWS Auto Scaling and AWS Lambda are examples of services that help automate these tasks, ensuring that resources are provisioned dynamically based on demand and that functions are executed automatically in response to specific events.
Furthermore, DevOps practices foster a culture of collaboration and continuous improvement. By using AWS DevOps tools, SMEs can enhance communication and collaboration between development and operations teams, leading to faster problem resolution and more reliable deployments. The integration of monitoring and logging tools, such as Amazon CloudWatch and AWS X-Ray, provides visibility into the performance and health of applications, enabling teams to identify and address issues proactively.
Managed services play a vital role in enhancing operational efficiency by offloading the management of infrastructure and applications to AWS. By leveraging managed services, SMEs can focus on their core business activities while AWS handles the operational aspects, such as maintenance, updates, and scaling.
Chou highlights the value creation potential of cloud computing through managed services, which enable businesses to achieve operational efficiency and agility [12]. AWS offers a wide range of managed services that cater to different aspects of IT infrastructure and application management.
For instance, Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service) is a managed database service that automates time-consuming administrative tasks such as hardware provisioning, database setup, patching, and backups. By using Amazon RDS, SMEs can reduce the complexity of managing databases and ensure high availability and scalability without the need for dedicated database administrators.
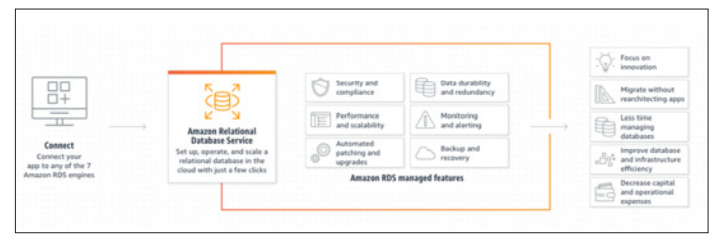
Accessed from: https://aws.amazon.com/rds/
Similarly, Amazon ECS (Elastic Container Service) and Amazon EKS (Elastic Kubernetes Service) provide managed container orchestration services that simplify the deployment and management of containerized applications. These services handle the underlying infrastructure, allowing SMEs to focus on developing and running their applications. The use of containers and managed orchestration services enables faster deployment cycles, improved resource utilization, and greater scalability.
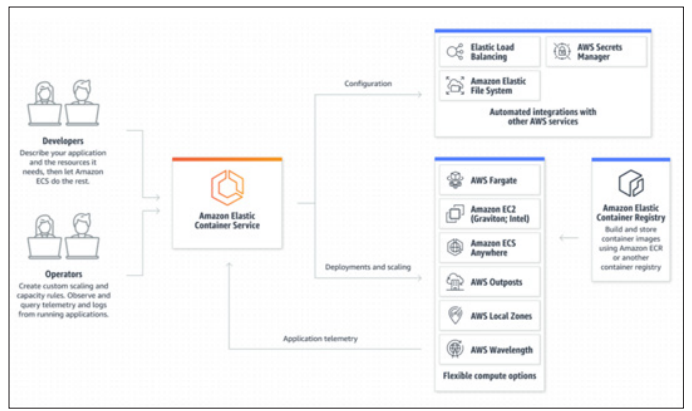
Accessed from: https://aws.amazon.com/ecs/
Dillon et al. emphasizes the importance of leveraging managed services to address the challenges of cloud computing, such as scalability and resource management [11]. AWS Lambda, a serverless computing service, is another example of a managed service that abstracts the underlying infrastructure, allowing developers to run code without provisioning or managing servers. This serverless model not only reduces operational overhead but also enables rapid scaling and cost optimization based on actual usage.
Managed services also enhance security and compliance by incorporating best practices and adhering to industry standards. For example, AWS Managed Services (AMS) provides a comprehensive framework for managing and operating AWS environments securely and efficiently. AMS includes features such as automated patching, backup management, and security monitoring, ensuring that SMEs meet their compliance requirements while maintaining operational efficiency.
Effective monitoring and performance management are critical for ensuring the reliability and efficiency of applications and infrastructure in the cloud. AWS provides a suite of monitoring and performance management tools that enable SMEs to gain insights into their cloud environments, detect issues proactively, and optimize performance.
Armbrust et al. highlight the importance of monitoring in cloud computing, noting that visibility into the performance and health of applications is essential for maintaining operational efficiency [10]. Amazon CloudWatch is a comprehensive monitoring service that collects and tracks metrics, logs, and events from AWS resources and applications. CloudWatch allows SMEs to create custom dashboards, set alarms, and automate responses to specific conditions, enabling real-time monitoring and alerting.
In addition to CloudWatch, AWS X-Ray provides deep visibility into the performance of distributed applications. X-Ray helps developers analyze and debug complex applications by tracing requests as they travel through the various services that make up an application. This end-to-end visibility allows SMEs to identify performance bottlenecks, diagnose errors, and optimize their application architecture.
Dillon et al. emphasizes the challenges of managing performance in cloud environments, particularly for distributed applications [11]. By using AWS monitoring and performance management tools, SMEs can address these challenges and ensure that their applications perform optimally. AWS also offers the AWS Trusted Advisor service, which provides real-time guidance to help businesses optimize their AWS environment for performance, security, and cost-efficiency.
Chou discusses the role of performance management in value creation, noting that businesses need to continuously monitor and optimize their cloud resources to achieve maximum efficiency [12]. AWS provides additional tools such as AWS Cost Explorer and AWS Compute Optimizer, which offer insights into resource utilization and recommendations for cost and performance optimization. By leveraging these tools, SMEs can ensure that their resources are allocated efficiently and that their applications deliver consistent performance.
Furthermore, integrating monitoring and performance management with automation and DevOps practices can enhance operational efficiency. For example, by using CloudWatch alarms and AWS Lambda, SMEs can automate responses to performance issues, such as scaling up resources or restarting services. This proactive approach to performance management ensures that applications remain available and performant, even during periods of high demand.
Encouraging Experimentation and Rapid Prototyping Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides a robust platform for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to foster innovation through experimentation and rapid prototyping. The ability to quickly test ideas and develop prototypes is crucial for businesses looking to stay competitive and adapt to changing market conditions. AWS’s flexible and scalable infrastructure, combined with a wide array of development tools, enables SMEs to experiment without significant upfront investment.
One of the key advantages of AWS is its pay-as-you-go pricing model, which allows businesses to experiment with new ideas without committing to long-term investments. This model reduces the financial risk associated with innovation, as SMEs can scale resources up or down based on their needs. Brynjolfsson and McAfee highlight that the cloud's flexibility is particularly beneficial for fostering innovation, as it allows companies to allocate resources dynamically and respond quickly to new opportunities [13].
AWS services such as AWS Lambda and Amazon EC2 enable rapid deployment of applications and services, allowing developers to iterate quickly and refine their prototypes. AWS Lambda supports serverless computing, which eliminates the need to manage underlying infrastructure. This allows developers to focus on writing code and deploying applications, thereby accelerating the development process.
Moreover, AWS offers a suite of development and deployment tools that support continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD). Tools like AWS Code Pipeline, AWS Code Build, and AWS Code Deploy automate the build, test, and deployment processes, enabling SMEs to release new features and updates rapidly. Davenport and Ronanki emphasize the importance of rapid prototyping and iterative development in driving innovation, noting that these practices allow businesses to quickly validate ideas and bring new products to market [14].
Additionally, AWS’s extensive ecosystem of services and third- party integrations provides a rich environment for experimentation. Services such as Amazon SageMaker for machine learning, AWS IoT Core for Internet of Things (IoT) applications, and Amazon Polly for text-to-speech conversion enable SMEs to incorporate advanced technologies into their prototypes. This capability not only enhances the functionality of their applications but also opens up new avenues for innovation.
The integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT) is a key driver of innovation for SMEs. AWS provides a comprehensive suite of services that make these technologies accessible and affordable, enabling businesses to leverage cutting- edge tools to enhance their operations and develop innovative solutions.
AI and ML are transforming industries by enabling businesses to derive insights from data, automate processes, and improve decision-making. AWS offers powerful AI and ML services such as Amazon SageMaker, which simplifies the process of building, training, and deploying machine learning models. Brynjolfsson and McAfee highlight that AI and ML are becoming essential components of modern business strategies, as they enable companies to harness data for competitive advantage [13].
Amazon SageMaker provides a fully managed environment for data scientists and developers to collaborate on ML projects. It includes features such as built-in algorithms, automated model tuning, and deployment capabilities, making it easier for SMEs to implement machine learning without requiring extensive expertise. Additionally, AWS offers pre-trained AI services such as Amazon Rekognition for image and video analysis, Amazon Comprehend for natural language processing, and Amazon Lex for building conversational interfaces.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is another area where AWS excels, offering services that enable businesses to connect, manage, and analyze data from IoT devices. AWS IoT Core provides secure and scalable connectivity for IoT devices, allowing SMEs to collect and process data in real time. This capability is particularly valuable for industries such as manufacturing, agriculture, and healthcare, where IoT can drive efficiency and innovation.
Davenport and Ronanki discuss the real-world applications of AI and IoT, emphasizing that these technologies can lead to significant improvements in operational efficiency and customer experiences [14]. By integrating IoT with AI and ML, SMEs can develop intelligent systems that monitor and optimize processes, predict maintenance needs, and personalize customer interactions.
Moreover, AWS provides edge computing solutions such as AWS IoT Greengrass, which allows businesses to run IoT applications locally on devices, enabling real-time processing and reducing latency. This is particularly important for applications that require immediate responses, such as industrial automation and smart cities.
The combination of AI, ML, and IoT capabilities on AWS empowers SMEs to innovate at scale. By leveraging these technologies, businesses can create smart products, enhance operational efficiency, and deliver personalized experiences to their customers. The accessibility and scalability of AWS services ensure that even small businesses can experiment with and benefit from these advanced technologies.
Numerous SMEs have successfully leveraged AWS to drive innovation and achieve significant business outcomes. These case studies demonstrate the potential of AWS to transform operations, enhance customer experiences, and create new revenue streams.
One notable example is the healthcare technology company, MedAware. MedAware uses AWS to develop and deploy its AI-driven medication safety solutions. By leveraging Amazon SageMaker, MedAware can analyze vast amounts of medical data to detect potential medication errors and provide real- time alerts to healthcare providers. This innovative approach not only improves patient safety but also reduces healthcare costs. Brynjolfsson and McAfee note that AI-driven solutions in healthcare are revolutionizing patient care by providing insights that were previously unattainable [13].
Another example is the agricultural technology startup, Taranis. Taranis uses AWS IoT Core and Amazon SageMaker to develop precision agriculture solutions that help farmers optimize crop yields. By collecting data from IoT sensors and using machine learning models to analyze this data, Taranis provides farmers with actionable insights on irrigation, fertilization, and pest control. This data-driven approach enhances agricultural productivity and sustainability. Davenport and Ronanki highlight the transformative impact of IoT and AI in agriculture, noting that these technologies enable more efficient and sustainable farming practices [14].
In the retail sector, the e-commerce platform, Zilingo, leverages AWS to enhance its operations and customer experience. Zilingo uses a combination of AWS services, including Amazon EC2, Amazon S3, and Amazon Redshift, to build a scalable and reliable infrastructure. Additionally, the company utilizes Amazon Personalize to deliver personalized product recommendations to its customers, improving engagement and sales. By integrating advanced technologies into its platform, Zilingo can compete with larger players and provide a superior shopping experience.
These case studies illustrate how SMEs across different industries are using AWS to innovate and achieve competitive advantages. The flexibility, scalability, and advanced capabilities of AWS enable these businesses to experiment with new ideas, integrate cutting-edge technologies, and rapidly bring innovative solutions to market.
The adoption of Amazon Web Services (AWS) by small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) presents both significant opportunities and notable challenges. This study has highlighted the critical benefits of AWS, including scalability, cost efficiency, enhanced security, and access to advanced technologies. However, SMEs also face obstacles such as financial constraints, skill gaps, integration with legacy systems, and data security concerns. Effective strategies and best practices for overcoming these challenges include optimizing resource allocation, cost management, leveraging AWS support and training programs, and enhancing operational efficiency through automation, managed services, and robust monitoring. Furthermore, AWS facilitates innovation through experimentation, rapid prototyping, and the integration of advanced technologies like AI, ML, and IoT.
The implications of adopting AWS for SMEs are profound, offering a pathway to enhanced operational efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness. Below are the key implications drawn from the findings of this study:
AWS enables SMEs to optimize their resource allocation through services like AWS Auto Scaling and AWS Lambda. These tools allow businesses to dynamically adjust their computing resources based on demand, ensuring efficient utilization and reducing waste.
By utilizing AWS managed services such as Amazon RDS and Amazon ECS, SMEs can offload routine maintenance tasks, allowing them to focus on core business activities. This shift not only improves operational efficiency but also reduces the need for extensive in-house IT expertise.
The pay-as-you-go pricing model of AWS, coupled with cost management tools like AWS Cost Explorer and AWS Budgets, allows SMEs to maintain control over their cloud spending. This financial flexibility is crucial for businesses operating on tight budgets.
Leveraging Reserved Instances and Savings Plans can provide significant cost savings, making AWS an economically viable option for long-term projects and consistent workloads.
AWS’s comprehensive security framework, including services like AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) and AWS Shield, helps SMEs enhance their security posture. By adhering to best practices and leveraging AWS’s compliance certifications, SMEs can ensure regulatory compliance and protect sensitive data.
The shared responsibility model of AWS clarifies the division of security tasks between AWS and the customer, helping SMEs understand their role in securing their applications and data.
AWS’s extensive suite of services supports rapid prototyping and experimentation, enabling SMEs to innovate without significant upfront investment. This capability is critical for businesses looking to develop new products and services quickly.
The integration of advanced technologies such as AI, ML, and IoT through AWS services like Amazon SageMaker and AWS IoT Core empowers SMEs to develop intelligent applications and optimize their operations. This technological edge can lead to improved customer experiences and new revenue streams.
AWS training and certification programs provide SMEs with the resources needed to build a skilled workforce capable of managing and optimizing AWS environments. This investment in skill development is essential for sustaining long-term success in the cloud.
AWS support plans offer various levels of technical assistance, ensuring that SMEs have access to expert guidance and troubleshooting when needed. This support can mitigate the risks associated with cloud adoption and ensure smooth operations.
While this study provides a comprehensive overview of the benefits and challenges associated with AWS adoption for SMEs, there are several areas where further research could provide additional insights and value. Future research directions include:
A detailed comparative study of AWS with other leading cloud service providers like Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform could provide SMEs with a broader perspective on the best fit for their specific needs. Such research could explore differences in pricing models, service offerings, performance, and customer support.
Conducting longitudinal studies that track the cost efficiency of AWS adoption over an extended period could provide valuable insights into the long-term financial implications for SMEs. This research could help businesses better understand the total cost of ownership (TCO) and identify strategies for sustained cost management.
Investigating the correlation between cloud adoption and business growth metrics such as revenue, market share, and customer satisfaction would offer a clearer picture of the tangible benefits of AWS. This research could include case studies of SMEs that have successfully leveraged AWS to achieve significant business milestones.
Developing sector-specific case studies that examine how different industries utilize AWS can provide tailored insights and best practices. For instance, exploring AWS adoption in healthcare, finance, retail, and manufacturing could highlight unique challenges and innovative solutions relevant to each sector.
In-depth research on the security and compliance challenges faced by SMEs in highly regulated industries would be valuable. This could include examining the effectiveness of AWS’s security features and compliance certifications in meeting industry-specific regulatory requirements.
Studying the human factors involved in cloud adoption, such as organizational culture, change management, and employee resistance, could provide a more holistic understanding of the barriers to successful cloud migration. This research could identify strategies for fostering a cloud-friendly culture and ensuring smooth transitions.
Exploring the future trends in cloud computing, such as the impact of emerging technologies like edge computing, quantum computing, and blockchain, would help SMEs stay ahead of the curve. Researching how AWS is evolving to incorporate these technologies and their potential applications could provide forward-looking insights.
Investigating the environmental impact of cloud computing, particularly in terms of energy consumption and carbon footprint, could provide important insights for SMEs committed to sustainability. This research could examine AWS’s efforts to promote green cloud practices and the benefits of adopting such practices.
